Product Description
Precision Shaft by CNC Turning Machining
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price-quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
Inspection equipment :
Certificate:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT01-IT5 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How does the design of a spline shaft affect its performance?
The design of a spline shaft plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission:
The design of the spline shaft directly affects its ability to transmit torque efficiently. Factors such as the spline profile, number of splines, and engagement length influence the torque-carrying capacity of the shaft. A well-designed spline profile with optimized dimensions ensures maximum contact area and load distribution, resulting in improved torque transmission.
2. Load Distribution:
A properly designed spline shaft distributes the applied load evenly across the engagement surfaces. This helps to minimize stress concentrations and prevents localized wear or failure. The design should consider factors such as spline profile geometry, tooth form, and surface finish to achieve optimal load distribution and enhance the overall performance of the shaft.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
Spline shafts can accommodate a certain degree of misalignment between the mating components. The design of the spline profile can incorporate features that allow for angular or parallel misalignment, ensuring effective power transmission even under misaligned conditions. Proper design considerations help maintain smooth operation and prevent excessive stress or premature failure.
4. Torsional Stiffness:
The design of the spline shaft influences its torsional stiffness, which is the resistance to twisting under torque. A stiffer shaft design reduces torsional deflection, improves torque response, and enhances the system’s overall performance. The shaft material, diameter, and spline profile all contribute to achieving the desired torsional stiffness.
5. Fatigue Resistance:
The design of the spline shaft should consider fatigue resistance to ensure long-term durability. Fatigue failure can occur due to repeated or cyclic loading. Proper design practices, such as optimizing the spline profile, selecting appropriate materials, and incorporating suitable surface treatments, can enhance the fatigue resistance of the shaft and extend its service life.
6. Surface Finish and Lubrication:
The surface finish of the spline shaft and the lubrication used significantly impact its performance. A smooth surface finish reduces friction, wear, and the potential for corrosion. Proper lubrication ensures adequate film formation, reduces heat generation, and minimizes wear. The design should incorporate considerations for surface finish requirements and lubrication provisions to optimize the shaft’s performance.
7. Environmental Considerations:
The design should take into account the specific environmental conditions in which the spline shaft will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, exposure to chemicals, or abrasive particles can affect the shaft’s performance and longevity. Suitable material selection, surface treatments, and sealing mechanisms can be incorporated into the design to withstand the environmental challenges.
8. Manufacturing Feasibility:
The design of the spline shaft should also consider manufacturing feasibility and cost-effectiveness. Complex designs may be challenging to produce or require specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in increased production costs. Balancing design complexity with manufacturability is crucial to ensure a practical and efficient manufacturing process.
By considering these design factors, engineers can optimize the performance of spline shafts, resulting in enhanced torque transmission, improved load distribution, misalignment compensation, torsional stiffness, fatigue resistance, surface finish, and environmental compatibility. A well-designed spline shaft contributes to the overall efficiency, reliability, and longevity of the mechanical system in which it is used.

How do spline shafts handle variations in load capacity and weight?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in load capacity and weight in mechanical systems. Here’s how they accomplish this:
1. Material Selection:
Spline shafts are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel or alloy, chosen for their ability to withstand heavy loads and provide durability. The selection of materials takes into account factors such as tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance to ensure the shaft can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
2. Engineering Design:
Spline shafts are designed with consideration for the anticipated loads and weights they will encounter. The dimensions, profile, and number of splines are determined based on the expected torque requirements and the magnitude of the applied loads. By carefully engineering the design, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight while maintaining structural integrity and reliable performance.
3. Load Distribution:
The interlocking engagement of spline shafts allows for effective load distribution along the length of the shaft. This helps distribute the applied loads evenly, preventing localized stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of deformation or failure. By distributing the load, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight without compromising their performance.
4. Structural Reinforcement:
In applications with higher load capacities or heavier weights, spline shafts may incorporate additional structural features to enhance their strength. This can include thicker spline teeth, larger spline diameters, or reinforced sections along the shaft. By reinforcing critical areas, spline shafts can handle increased loads and weights while maintaining their integrity.
5. Lubrication and Surface Treatment:
Proper lubrication is essential for spline shafts to handle variations in load capacity and weight. Lubricants reduce friction between the mating surfaces, minimizing wear and preventing premature failure. Additionally, surface treatments such as coatings or heat treatments can enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the spline shaft, improving its ability to handle varying loads and weights.
6. Testing and Validation:
Spline shafts undergo rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet the specified load capacity and weight requirements. This may involve laboratory testing, simulation analysis, or field testing under real-world conditions. By subjecting spline shafts to thorough testing, manufacturers can verify their performance and ensure they can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
Overall, spline shafts are designed and engineered to handle variations in load capacity and weight by utilizing appropriate materials, optimizing the design, distributing loads effectively, incorporating structural reinforcement when necessary, implementing proper lubrication and surface treatments, and conducting thorough testing and validation. These measures enable spline shafts to reliably transmit torque and handle varying loads in diverse mechanical applications.
What are the key components and design features of a spline shaft?
A spline shaft consists of several key components and incorporates specific design features to ensure its functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Shaft Body:
The main component of a spline shaft is the shaft body, which provides the structural integrity and serves as the base for the spline features. The shaft body is typically cylindrical in shape and made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, or other alloyed metals. The material selection depends on factors like the application requirements, torque loads, and environmental conditions.
2. Splines:
The splines are the key design feature of a spline shaft. They are ridges or teeth that are machined onto the surface of the shaft. The splines create the interlocking mechanism with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. The number, size, and shape of the splines can vary depending on the application requirements and design specifications.
3. Spline Profile:
The spline profile refers to the specific shape or geometry of the splines. Common types of spline profiles include involute, straight-sided, and serrated. The spline profile is chosen based on factors such as the torque transmission requirements, load distribution, and the desired engagement characteristics with mating components. The spline profile ensures optimal contact and torque transfer between the spline shaft and the mating component.
4. Spline Fit:
The spline fit refers to the dimensional relationship between the spline shaft and the mating component. It determines the clearance or interference between the splines, ensuring proper engagement and transmission of torque. The spline fit can be categorized into different classes, such as clearance fit, transition fit, or interference fit, based on the desired level of clearance or interference.
5. Surface Finish:
The surface finish of the spline shaft is crucial for its performance. The splines and the shaft body should have a smooth and consistent surface finish to minimize friction, wear, and the risk of stress concentrations. The surface finish can be achieved through machining, grinding, or other surface treatment methods to meet the required specifications.
6. Lubrication:
To ensure smooth operation and reduce wear, lubrication is often employed for spline shafts. Lubricants with appropriate viscosity and lubricating properties are applied to the spline interface to minimize friction, dissipate heat, and prevent premature wear or damage to the splines and mating components. Lubrication also helps in maintaining the functionality and prolonging the service life of the spline shaft.
7. Machining Tolerances:
Precision machining is critical for spline shafts to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and ensure proper engagement with mating components. Tight machining tolerances are maintained during the manufacturing process to ensure the spline profile, dimensions, and surface finish meet the specified design requirements. This ensures the interchangeability and compatibility of spline shafts in various applications.
In summary, the key components and design features of a spline shaft include the shaft body, splines, spline profile, spline fit, surface finish, lubrication, and machining tolerances. These elements work together to enable torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution while ensuring the functionality, durability, and performance of the spline shaft.


editor by CX 2024-05-17
China high quality Rotor Shaft Manufacturing 16mm Machinery Part Spline Shaft Price
Product Description
Chrome plated induction linear shaft, hollow shaft and flexible linear shaft
Company Profile
HangZhou Wangong Precision Machinery Co., Ltd.
About US: Professional producing Ball screw, Linear guide, linear shaft, Linear roller guide and linear motion bearings
HangZhou Wangong Precision Machinery Co., Ltd was founded in 2008 and is located in HangZhou City, ZHangZhoug Pro. China. We ahve built a R&D and profuction base of more than 52000m2 , Our expertise lies in manufacturing precision transmission components, As a distinguished high-tech enterprise, we seamlessly integrate research and development, production, sales, and service. We have successfully incorporated advanced equipment and cutting-edge technologies from renowned countries like Germany, Japan and ZheJiang .
Product Description
1, Linear shaft description
ERSK Linear offers linear shafting in a variety of different options to meet a wide range of customer needs. Available in hardened steel, CK45 material steel, SUJ2 material steel, hollow steel , inch and metric, Simplicity Shafting maintains the ideal surface finish for linear plain bearings and ball bearings.
· CHINAMFG round shafting is available in inch sizes from 3/16″ thru 4″ and metric sizes from 3 mm thru 80 mm
· Machining available CHINAMFG request
High Reliability
ERSK linear shaft has very straight quality control standards covering every production process. With proper lubrication and use, trouble-free operation for an extended period of time is possible.
Smooth Operation
The high efficiency of linear shaft is vastly superior to conventional shaft. The torque required is less than 30%. Linear motion can be easily changed from rotary motion.
High Durability
Rigidly selected materials, intensive heat treating and processing techniques, backed by years of experience,have resulted in the most durable linear shaft manufactured.
Induction linear shaft, Flexible linear shaft,
linear bearings shaft, hollow linear shaft,
hardened linear shaft, chromed linear shaft
Application
For delicate application in industrial application, machine tool and automation application.
2, There are 3 kinds of linear shaft in our stock:
| Flexible linear shfat | Induction linear shaft | Hollow linear shaft |
3, Linear shaft features
|
Items |
Linear shaft |
Flexible shaft |
Hollow shaft |
|
Material |
CK45, SUJ2 |
CK45 |
SUJ2 |
|
Heat treatment |
Induction hardened |
Not hardened |
Induction hardened |
|
Surface hardness |
HRC58±2 |
HRC15±3 |
HRC60±2 |
|
Surface treated |
Hard chrome plated |
Hard chrome plated |
Hard chrome plated |
|
Precision |
h7, g6, h6 |
h7, g6 |
h7, g6, h6 |
|
Roundness |
Max3.0µm |
Max3.0µm |
Max3.0µm |
|
Straightness |
Max5.0µm |
Max5.0µm |
Max5.0µm |
|
Chrome thickness |
20-30µm |
30µm |
30µm |
|
Roughness |
Max1.5µm |
Max1.5µm |
Max1.5µm |
|
Process machinized |
Threading, reduced shaft dia,coaxial holes drilled and tapped, flats-single or multiple, key way, snap ring grooves, radial holes drilled and tapped, chamfering |
||
4, There are many different kinds of machining process we can do:
Processing machinized Flats—Single or Multiple
Processing machinized Radial holes drilled and tapped
Processing machinized Coaxial holes drilled and tapped
Processing machinized key way
Processing machinized Reduced shaft dia and threading
Processing machinized Snap ring grooves
5,Test the quality according to cusdifferent requirements
Straight the linear shaft straightness:
We control the traighness 0.05mm of linear shaft 300mm
Test hardness:
S45C materail induction linear shaft, the hardness is HRC55-58
GCr15 (SUJ2) materail induction linear shaft, the hardness is HRC58-63
If flexible shaft, the hardness is based on the shaft material itself
Test linear shaft surface roughness
the max roughness is Ra0.4um
Test the linear shaft dia precision, as usually, h7 is the normal tolerance in our stock, But we can offer g6, h6 precision too. if any special tolerance, we are able to customize them for you.
6, Data sheet
Related products
ERSK manufacturer main products
Our Advantages
As a distinguished high-tech enterprise, we seamlessly integrate research and development, production, sales, and service. We have successfully incorporated advanced equipment and cutting-edge technologies from renowned countries like Germany, Japan, and ZheJiang . Our commitment to innovation has led to the acquisition of multiple product design patents, and we proudly adhere to ISO9001 certification standards.
Our service
Our Team:
Professional technicians, high-quality production workers, 24-hour salespersons
OUR PHILOSOPHY:
Integrity is at the core of our values, and providing excellent
service is our top priority. We begin by understanding your
needs and strive to ensure your utmost satisfaction, forging a mutually beneficial relationship.
OUR MISSION:
Through technology and innovation, we strive to enhance
product quality and deliver exceptional products and services
to you.
OUR VISION:
We are firmly dedicated to CHINAMFG the pinnacle of highquality standards and venturing into the realm of world-class
advanced manufacturing industries.
We are excited about the opportunity to work with you and
exceed your expectations.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Gcr15 |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Samples: |
US$ 3/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | Order Sample chrome plated linear shaft
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What safety considerations should be kept in mind when working with spline shafts?
Working with spline shafts requires adherence to certain safety considerations to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the machinery or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
When working with spline shafts, individuals should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with lubricants.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Prior to performing any maintenance or repair work on machinery or equipment involving spline shafts, proper lockout/tagout procedures should be followed. This involves isolating the power source, de-energizing the system, and securing it with lockout devices or tags to prevent accidental startup or release of stored energy.
3. Training and Competence:
Only trained and competent personnel should work with spline shafts. They should have a thorough understanding of the machinery or equipment, including the operation, maintenance, and safety procedures specific to spline shafts. Adequate training and knowledge help minimize the risk of accidents or improper handling.
4. Proper Handling and Lifting Techniques:
When moving or lifting machinery components that include spline shafts, proper techniques should be employed. This includes using appropriate lifting equipment, maintaining a stable posture, and avoiding sudden movements that could cause strain or injury.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Spline shafts should be regularly inspected for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Any abnormalities should be addressed promptly by qualified personnel. Routine maintenance, such as lubrication and cleaning, should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
6. Correct Installation and Alignment:
During installation or replacement of spline shafts, proper alignment and fit should be ensured. The shafts should be correctly seated and engaged with the mating components, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Improper installation or misalignment can lead to premature wear, excessive stress, or failure of the spline shafts.
7. Hazardous Environments:
When spline shafts are used in hazardous environments, such as those with flammable substances, extreme temperatures, or high vibrations, additional safety measures may be required. These may include explosion-proof enclosures, temperature monitoring, or vibration damping systems.
8. Emergency Procedures:
Emergency procedures should be established and communicated to all personnel working with spline shafts. This includes knowing the location of emergency stops, emergency shutdown procedures, and the contact information for emergency response personnel.
9. Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations regarding the installation, operation, and maintenance of spline shafts. The manufacturer’s instructions provide specific safety information and precautions tailored to their product.
By taking these safety considerations into account and implementing appropriate measures, the risks associated with working with spline shafts can be minimized. Safety should always be a top priority when dealing with machinery or equipment that incorporates spline shafts.
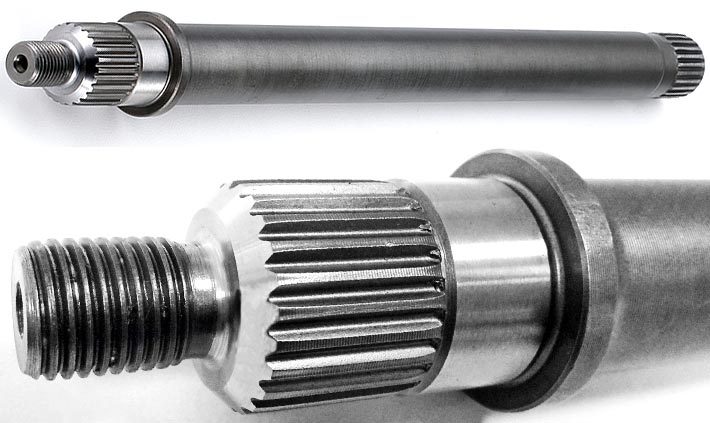

Can spline shafts be repaired or maintained when necessary?
Yes, spline shafts can be repaired and maintained when necessary to ensure their continued functionality and performance. Here are some ways spline shafts can be repaired and maintained:
1. Inspection and Assessment:
When an issue is suspected with a spline shaft, the first step is to conduct a thorough inspection. This involves examining the shaft for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Special attention is given to the spline teeth, which may show signs of wear or deformation. Through inspection and assessment, the extent of the repair or maintenance required can be determined.
2. Spline Tooth Repair:
If the spline teeth are damaged or worn, they can be repaired or replaced. Repair methods may include re-machining the teeth to restore their original profile, filling and reshaping the worn areas using specialized welding techniques, or replacing the damaged section of the spline shaft. The specific repair method depends on the severity of the damage and the material of the spline shaft.
3. Lubrication and Cleaning:
Regular lubrication and cleaning are essential for maintaining spline shafts. Lubricants help reduce friction and wear between the mating surfaces, while cleaning removes contaminants that can affect the spline’s engagement. During maintenance, old lubricants are removed, and fresh lubricants are applied to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature failure.
4. Surface Treatment:
If the spline shaft undergoes wear or corrosion, surface treatment can be applied to restore its condition. This may involve applying coatings or treatments to enhance the hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion resistance of the spline shaft. Surface treatments can improve the longevity and performance of the spline shaft, reducing the need for frequent repairs.
5. Balancing and Alignment:
If a spline shaft is experiencing vibration or misalignment issues, it may require balancing or realignment. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the shaft to minimize vibrations, while alignment ensures proper mating and engagement with other components. Balancing and alignment procedures help optimize the performance and longevity of the spline shaft.
6. Replacement:
In cases where the spline shaft is severely damaged or worn beyond repair, replacement may be necessary. Replacement spline shafts can be sourced from manufacturers or specialized suppliers who can provide shafts that meet the required specifications and tolerances.
It’s important to note that the repair and maintenance of spline shafts should be carried out by qualified professionals with expertise in precision machining and mechanical systems. They have the knowledge and tools to properly assess, repair, or replace spline shafts, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the system in which they are used.
By implementing regular maintenance and timely repairs, spline shafts can be kept in optimal condition, extending their lifespan and maintaining their performance in various mechanical applications.

What are the key components and design features of a spline shaft?
A spline shaft consists of several key components and incorporates specific design features to ensure its functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Shaft Body:
The main component of a spline shaft is the shaft body, which provides the structural integrity and serves as the base for the spline features. The shaft body is typically cylindrical in shape and made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, or other alloyed metals. The material selection depends on factors like the application requirements, torque loads, and environmental conditions.
2. Splines:
The splines are the key design feature of a spline shaft. They are ridges or teeth that are machined onto the surface of the shaft. The splines create the interlocking mechanism with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. The number, size, and shape of the splines can vary depending on the application requirements and design specifications.
3. Spline Profile:
The spline profile refers to the specific shape or geometry of the splines. Common types of spline profiles include involute, straight-sided, and serrated. The spline profile is chosen based on factors such as the torque transmission requirements, load distribution, and the desired engagement characteristics with mating components. The spline profile ensures optimal contact and torque transfer between the spline shaft and the mating component.
4. Spline Fit:
The spline fit refers to the dimensional relationship between the spline shaft and the mating component. It determines the clearance or interference between the splines, ensuring proper engagement and transmission of torque. The spline fit can be categorized into different classes, such as clearance fit, transition fit, or interference fit, based on the desired level of clearance or interference.
5. Surface Finish:
The surface finish of the spline shaft is crucial for its performance. The splines and the shaft body should have a smooth and consistent surface finish to minimize friction, wear, and the risk of stress concentrations. The surface finish can be achieved through machining, grinding, or other surface treatment methods to meet the required specifications.
6. Lubrication:
To ensure smooth operation and reduce wear, lubrication is often employed for spline shafts. Lubricants with appropriate viscosity and lubricating properties are applied to the spline interface to minimize friction, dissipate heat, and prevent premature wear or damage to the splines and mating components. Lubrication also helps in maintaining the functionality and prolonging the service life of the spline shaft.
7. Machining Tolerances:
Precision machining is critical for spline shafts to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and ensure proper engagement with mating components. Tight machining tolerances are maintained during the manufacturing process to ensure the spline profile, dimensions, and surface finish meet the specified design requirements. This ensures the interchangeability and compatibility of spline shafts in various applications.
In summary, the key components and design features of a spline shaft include the shaft body, splines, spline profile, spline fit, surface finish, lubrication, and machining tolerances. These elements work together to enable torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution while ensuring the functionality, durability, and performance of the spline shaft.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China supplier Custom CNC Machining Turning Spline Bolt Nut Hollow Threaded Spindle Gear Steel Propeller Drive Shaft of Motorcycle Electric Motor Auto Generator Transmission
Product Description
| Basic Info. of Our Customized CNC Machining Parts | |
| Quotation | According To Your Drawings or Samples. (Size, Material, Thickness, Processing Content And Required Technology, etc.) |
| Tolerance | +/-0.005 – 0.01mm (Customizable) |
| Surface Roughness | Ra0.2 – Ra3.2 (Customizable) |
| Materials Available | Aluminum, Copper, Brass, Stainless Steel, Titanium, Iron, Plastic, Acrylic, PE, PVC, ABS, POM, PTFE etc. |
| Surface Treatment | Polishing, Surface Chamfering, Hardening and Tempering, Nickel plating, Chrome plating, zinc plating, Laser engraving, Sandblasting, Passivating, Clear Anodized, Color Anodized, Sandblast Anodized, Chemical Film, Brushing, etc. |
| Processing | Hot/Cold forging, Heat treatment, CNC Turning, Milling, Drilling and Tapping, Surface Treatment, Laser Cutting, Stamping, Die Casting, Injection Molding, etc. |
| Testing Equipment | Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) / Vernier Caliper/ / Automatic Height Gauge /Hardness Tester /Surface Roughness Teste/Run-out Instrument/Optical Projector, Micrometer/ Salt spray testing machine |
| Drawing Formats | PRO/E, Auto CAD, CHINAMFG Works , UG, CAD / CAM / CAE, PDF |
| Our Advantages | 1.) 24 hours online service & quickly quote and delivery. 2.) 100% quality inspection (with Quality Inspection Report) before delivery. All our products are manufactured under ISO 9001:2015. 3.) A strong, professional and reliable technical team with 16+ years of manufacturing experience. 4.) We have stable supply chain partners, including raw material suppliers, bearing suppliers, forging plants, surface treatment plants, etc. 5.) We can provide customized assembly services for those customers who have assembly needs. |
| Available Material | |
| Stainless Steel | SS201,SS301, SS303, SS304, SS316, SS416, etc. |
| Steel | mild steel, Carbon steel, 4140, 4340, Q235, Q345B, 20#, 45#, etc. |
| Brass | HPb63, HPb62, HPb61, HPb59, H59, H62, H68, H80, etc. |
| Copper | C11000, C12000,C12000, C36000 etc. |
| Aluminum | A380, AL2571, AL6061, Al6063, AL6082, AL7075, AL5052, etc. |
| Iron | A36, 45#, 1213, 12L14, 1215 etc. |
| Plastic | ABS, PC, PE, POM, Delrin, Nylon, PP, PEI, Peek etc. |
| Others | Various types of Titanium alloy, Rubber, Bronze, etc. |
| Available Surface Treatment | |
| Stainless Steel | Polishing, Passivating, Sandblasting, Laser engraving, etc. |
| Steel | Zinc plating, Oxide black, Nickel plating, Chrome plating, Carburized, Powder Coated, etc. |
| Aluminum parts | Clear Anodized, Color Anodized, Sandblast Anodized, Chemical Film, Brushing, Polishing, etc. |
| Plastic | Plating gold(ABS), Painting, Brushing(Acylic), Laser engraving, etc. |
FAQ:
Q1: Are you a trading company or a factory?
A1: We are a factory
Q2: How long is your delivery time?
A2: Samples are generally 3-7 days; bulk orders are 10-25 days, depending on the quantity and parts requirements.
Q3: Do you provide samples? Is it free or extra?
A3: Yes, we can provide samples, and we will charge you based on sample processing. The sample fee can be refunded after placing an order in batches.
Q4: Do you provide design drawings service?
A4: We mainly customize according to the drawings or samples provided by customers. For customers who don’t know much about drawing, we also provide design and drawing services. You need to provide samples or sketches.
Q5: What about drawing confidentiality?
A5: The processed samples and drawings are strictly confidential and will not be disclosed to anyone else.
Q6: How do you guarantee the quality of your products?
A6: We have set up multiple inspection procedures and can provide quality inspection report before delivery. And we can also provide samples for you to test before mass production.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, RoHS, GS, ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Standard: | DIN, ASTM, GOST, GB, JIS, ANSI, BS |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Material: | Metal |
| Application: | Metal Recycling Machine, Metal Cutting Machine, Metal Straightening Machinery, Metal Spinning Machinery, Metal Processing Machinery Parts, Metal forging Machinery, Metal Engraving Machinery, Metal Drawing Machinery, Metal Coating Machinery, Metal Casting Machinery |
| Tolerance: | +/-0.005 – 0.01mm |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
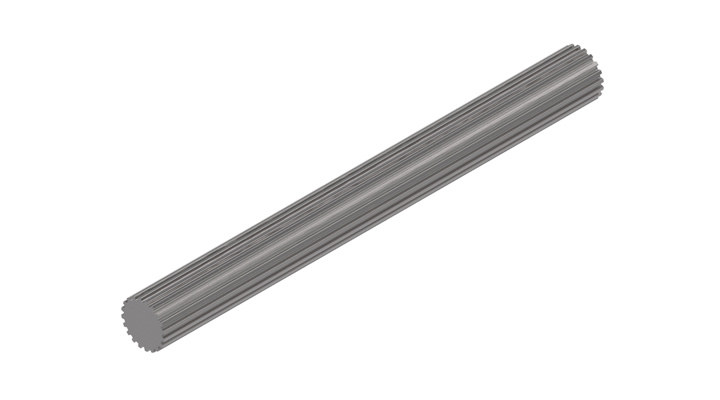

Can spline shafts be customized for specific machinery and equipment?
Yes, spline shafts can be customized to suit specific machinery and equipment requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Size and Length:
Spline shafts can be customized in terms of size and length to fit the dimensions of the machinery or equipment. Manufacturers can design spline shafts with the appropriate diameter, overall length, and spline length to ensure a proper fit within the system.
2. Spline Profile:
The spline profile can be customized based on the specific application. Different spline profiles, such as involute, serrated, or helical, can be used to optimize torque transmission, load distribution, and engagement characteristics based on the requirements of the machinery or equipment.
3. Number of Splines:
The number of splines on the shaft can be customized to match the mating component. The number of splines determines the engagement area and affects the torque-carrying capacity of the spline shaft. By adjusting the number of splines, manufacturers can tailor the spline shaft to the specific torque and load requirements of the machinery or equipment.
4. Material Selection:
The choice of material for spline shafts can be customized based on the operating conditions and environmental factors of the machinery or equipment. Different materials, such as alloy steels or stainless steels, can be selected to provide the necessary strength, durability, corrosion resistance, or other specific properties required for the application.
5. Surface Treatment:
The surface of spline shafts can be customized with various treatments to enhance their performance. Surface treatments like heat treatment, coating, or plating can be applied to improve hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion resistance based on the specific requirements of the machinery or equipment.
6. Tolerances and Fit:
Tolerances and fit between the spline shaft and mating components can be customized to achieve the desired clearance or interference fit. This ensures proper engagement, smooth operation, and optimal performance of the machinery or equipment.
7. Special Features:
In certain cases, spline shafts can be customized with additional features to meet specific needs. This may include the incorporation of keyways, threads, or other specialized features required for the machinery or equipment.
Manufacturers and engineers work closely with the machinery or equipment designers to understand the specific requirements and tailor the spline shafts accordingly. By considering factors such as size, spline profile, number of splines, material selection, surface treatment, tolerances, fit, and any special features, customized spline shafts can be developed to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the machinery or equipment.
It is important to consult with experienced spline shaft manufacturers or engineering professionals to determine the most suitable customization options for a particular machinery or equipment application.

Can spline shafts be repaired or maintained when necessary?
Yes, spline shafts can be repaired and maintained when necessary to ensure their continued functionality and performance. Here are some ways spline shafts can be repaired and maintained:
1. Inspection and Assessment:
When an issue is suspected with a spline shaft, the first step is to conduct a thorough inspection. This involves examining the shaft for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Special attention is given to the spline teeth, which may show signs of wear or deformation. Through inspection and assessment, the extent of the repair or maintenance required can be determined.
2. Spline Tooth Repair:
If the spline teeth are damaged or worn, they can be repaired or replaced. Repair methods may include re-machining the teeth to restore their original profile, filling and reshaping the worn areas using specialized welding techniques, or replacing the damaged section of the spline shaft. The specific repair method depends on the severity of the damage and the material of the spline shaft.
3. Lubrication and Cleaning:
Regular lubrication and cleaning are essential for maintaining spline shafts. Lubricants help reduce friction and wear between the mating surfaces, while cleaning removes contaminants that can affect the spline’s engagement. During maintenance, old lubricants are removed, and fresh lubricants are applied to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature failure.
4. Surface Treatment:
If the spline shaft undergoes wear or corrosion, surface treatment can be applied to restore its condition. This may involve applying coatings or treatments to enhance the hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion resistance of the spline shaft. Surface treatments can improve the longevity and performance of the spline shaft, reducing the need for frequent repairs.
5. Balancing and Alignment:
If a spline shaft is experiencing vibration or misalignment issues, it may require balancing or realignment. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the shaft to minimize vibrations, while alignment ensures proper mating and engagement with other components. Balancing and alignment procedures help optimize the performance and longevity of the spline shaft.
6. Replacement:
In cases where the spline shaft is severely damaged or worn beyond repair, replacement may be necessary. Replacement spline shafts can be sourced from manufacturers or specialized suppliers who can provide shafts that meet the required specifications and tolerances.
It’s important to note that the repair and maintenance of spline shafts should be carried out by qualified professionals with expertise in precision machining and mechanical systems. They have the knowledge and tools to properly assess, repair, or replace spline shafts, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the system in which they are used.
By implementing regular maintenance and timely repairs, spline shafts can be kept in optimal condition, extending their lifespan and maintaining their performance in various mechanical applications.
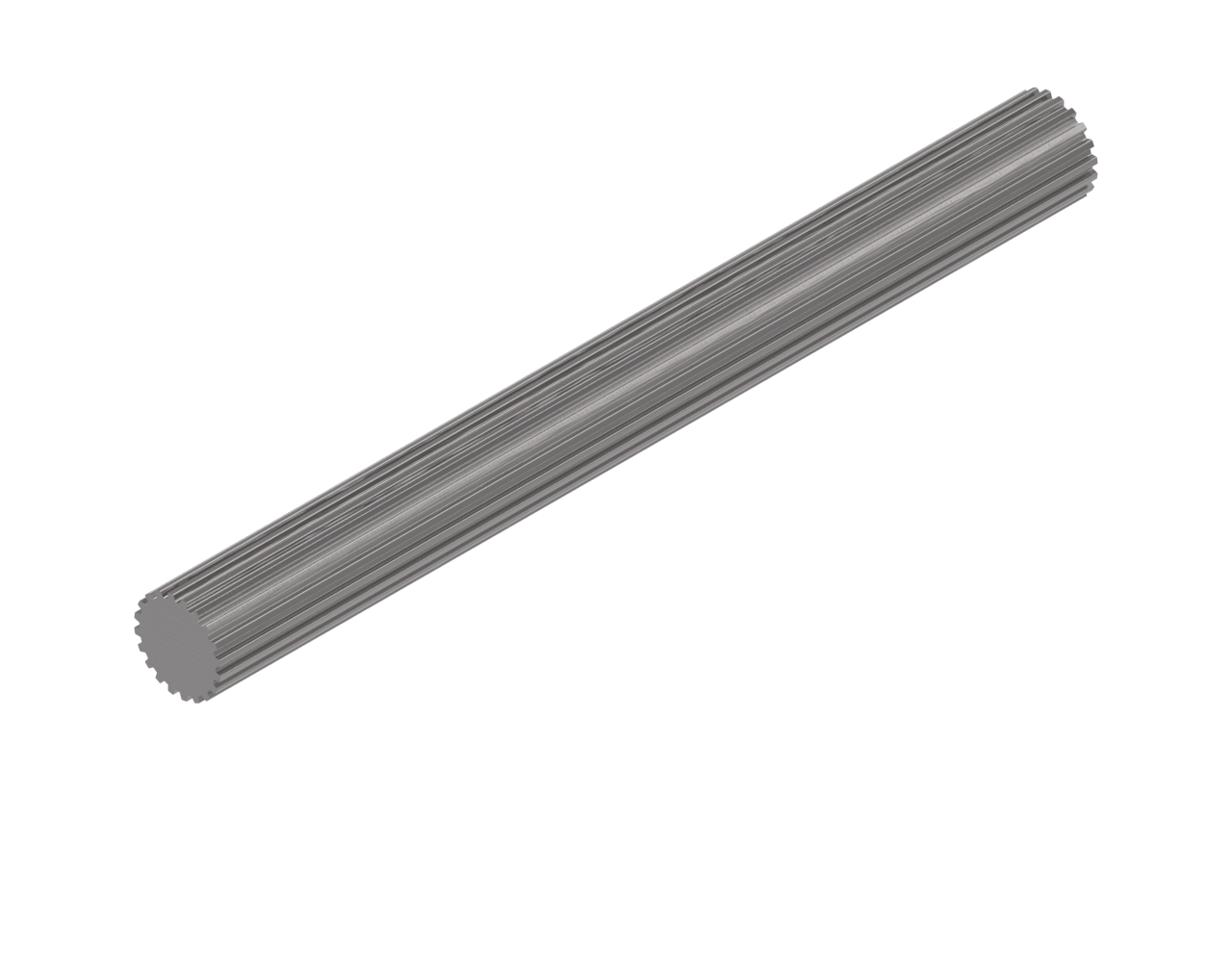

In which industries are spline shafts typically used?
Spline shafts find applications in a wide range of industries where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are critical. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry extensively uses spline shafts in various components and systems. They are found in transmissions, drivelines, steering systems, differentials, and axle assemblies. Spline shafts enable the transmission of torque, accommodate relative movement, and ensure efficient power transfer in vehicles.
2. Aerospace and Defense Industry:
Spline shafts are essential in the aerospace and defense industry. They are used in aircraft landing gear systems, actuation mechanisms, missile guidance systems, engine components, and rotor assemblies. The aerospace and defense sector relies on spline shafts for precise torque transfer, relative movement accommodation, and critical control mechanisms.
3. Industrial Machinery and Equipment:
Spline shafts are widely employed in industrial machinery and equipment. They are used in gearboxes, machine tools, pumps, compressors, conveyors, printing machinery, and packaging equipment. Spline shafts enable torque transmission, accommodate misalignments and vibrations, and ensure accurate movement and synchronization of machine components.
4. Agriculture and Farming:
The agriculture and farming industry extensively uses spline shafts in equipment such as tractors, harvesters, and agricultural implements. Spline shafts are found in power take-off (PTO) units, transmission systems, hydraulic mechanisms, and steering systems. They enable torque transfer, accommodate relative movement, and provide flexibility in agricultural machinery.
5. Construction and Mining:
In the construction and mining industries, spline shafts are used in equipment such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and drilling rigs. They are found in hydraulic systems, power transmission systems, and articulated mechanisms. Spline shafts facilitate torque transmission, accommodate misalignments, and enable efficient power transfer in heavy-duty machinery.
6. Marine and Offshore:
Spline shafts have applications in the marine and offshore industry. They are used in propulsion systems, thrusters, rudders, winches, and marine pumps. Spline shafts enable torque transmission in marine vessels and offshore equipment, accommodating axial and radial movement, and ensuring reliable power transfer.
7. Energy and Power Generation:
Spline shafts are utilized in the energy and power generation sector. They are found in turbines, generators, compressors, and other rotating equipment. Spline shafts enable torque transmission and accommodate relative movement in power generation systems, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
8. Rail and Transportation:
Spline shafts are employed in the rail and transportation industry. They are found in locomotives, railcar systems, and suspension mechanisms. Spline shafts enable torque transfer, accommodate movement and vibrations, and ensure precise control in rail and transportation applications.
These are just a few examples of the industries where spline shafts are typically used. Their versatility, torque transmission capabilities, and ability to accommodate relative movement make them vital components in various sectors that rely on efficient power transfer, flexibility, and precise control.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China Good quality High Precision Gear Shaft for Industrial Transmissions/Gearbox Drive Shaft with Spline by Knurling/Milling Factory Price Certificated
Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ25(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.2mm |
| Roundness | 0.1mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.8 |
| Straightness | 0.1mm |
| Hardness | HRC40-50 |
| Length | 98mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Torque Arm Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can spline shafts be customized for specific machinery and equipment?
Yes, spline shafts can be customized to suit specific machinery and equipment requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Size and Length:
Spline shafts can be customized in terms of size and length to fit the dimensions of the machinery or equipment. Manufacturers can design spline shafts with the appropriate diameter, overall length, and spline length to ensure a proper fit within the system.
2. Spline Profile:
The spline profile can be customized based on the specific application. Different spline profiles, such as involute, serrated, or helical, can be used to optimize torque transmission, load distribution, and engagement characteristics based on the requirements of the machinery or equipment.
3. Number of Splines:
The number of splines on the shaft can be customized to match the mating component. The number of splines determines the engagement area and affects the torque-carrying capacity of the spline shaft. By adjusting the number of splines, manufacturers can tailor the spline shaft to the specific torque and load requirements of the machinery or equipment.
4. Material Selection:
The choice of material for spline shafts can be customized based on the operating conditions and environmental factors of the machinery or equipment. Different materials, such as alloy steels or stainless steels, can be selected to provide the necessary strength, durability, corrosion resistance, or other specific properties required for the application.
5. Surface Treatment:
The surface of spline shafts can be customized with various treatments to enhance their performance. Surface treatments like heat treatment, coating, or plating can be applied to improve hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion resistance based on the specific requirements of the machinery or equipment.
6. Tolerances and Fit:
Tolerances and fit between the spline shaft and mating components can be customized to achieve the desired clearance or interference fit. This ensures proper engagement, smooth operation, and optimal performance of the machinery or equipment.
7. Special Features:
In certain cases, spline shafts can be customized with additional features to meet specific needs. This may include the incorporation of keyways, threads, or other specialized features required for the machinery or equipment.
Manufacturers and engineers work closely with the machinery or equipment designers to understand the specific requirements and tailor the spline shafts accordingly. By considering factors such as size, spline profile, number of splines, material selection, surface treatment, tolerances, fit, and any special features, customized spline shafts can be developed to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the machinery or equipment.
It is important to consult with experienced spline shaft manufacturers or engineering professionals to determine the most suitable customization options for a particular machinery or equipment application.

How do spline shafts handle variations in environmental conditions?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in environmental conditions and maintain their performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Temperature Variations:
Spline shafts are engineered to withstand a wide range of temperature variations. They are constructed from materials that exhibit good thermal stability, such as high-grade steels or alloys. These materials have low coefficients of thermal expansion, minimizing the effects of temperature changes on the shaft’s dimensional stability. Additionally, proper lubrication with temperature-resistant lubricants helps reduce friction and wear in the spline engagement, even under extreme temperature conditions.
2. Moisture and Corrosion Resistance:
Spline shafts can be designed to resist moisture and corrosion, ensuring their performance in humid or corrosive environments. Protective coatings, such as platings or surface treatments, can be applied to the shaft’s surfaces to enhance their resistance to moisture, oxidation, and corrosion. Additionally, selecting materials with inherent corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys, can further enhance the spline shaft’s ability to handle environmental conditions.
3. Dust and Contaminant Protection:
Spline shafts used in environments with high levels of dust, dirt, or contaminants can be equipped with protective measures. Seals, gaskets, or covers can be employed to prevent the ingress of particles into the spline engagement. These protective measures help maintain the integrity of the spline profile, minimize wear, and ensure smooth operation even in dirty or dusty conditions.
4. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication is essential for the reliable operation of spline shafts, especially in challenging environmental conditions. Lubricants with appropriate viscosity and additives can be selected to provide effective lubrication and protection against wear, friction, and corrosion. Regular maintenance and lubrication intervals should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the spline shaft.
5. Shock and Vibration Resistance:
Spline shafts are designed to withstand shock and vibration encountered in various applications. The spline engagement and shaft design can incorporate features such as tighter tolerances, increased contact area, or damping elements to minimize the effects of shock and vibration. Additionally, proper fastening and mounting techniques help secure the shaft and reduce the risk of loosening or failure due to dynamic loads.
6. Environmental Sealing:
In certain applications where spline shafts are exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as underwater or in chemical environments, environmental sealing can be employed. Sealing methods such as O-rings, gaskets, or specialized seals provide an additional barrier against external elements, ensuring the integrity and performance of the spline shaft.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Spline shafts used in specific industries or applications may need to comply with industry standards or regulations regarding environmental conditions. Manufacturers can design and test their spline shafts to meet these requirements, ensuring that the shafts can handle the specified environmental conditions and perform reliably.
By incorporating design considerations, appropriate materials, protective coatings, lubrication, and maintenance practices, spline shafts can effectively handle variations in environmental conditions. This enables them to maintain their functionality, performance, and longevity even in challenging operating environments.

How does a spline shaft differ from other types of shafts?
A spline shaft differs from other types of shafts in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Spline Structure:
A spline shaft features a series of ridges or teeth (splines) that are machined onto its surface. These splines create a precise and controlled interface with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. In contrast, other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, do not have the splines and rely on different mechanisms for torque transmission.
2. Torque Transmission and Relative Movement:
Unlike plain shafts or keyed shafts, which transmit torque through a frictional or mechanical connection, spline shafts allow for both torque transmission and relative movement between the shaft and mating components. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating an interlock that transfers rotational force while accommodating axial or radial displacement. This feature provides flexibility and is particularly useful in applications where misalignment or relative movement needs to be accommodated.
3. Load Distribution:
One of the advantages of spline shafts is their ability to distribute loads over a larger surface area. The multiple contact points created by the splines help distribute the applied load evenly along the shaft’s length. This load distribution minimizes stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure. In contrast, other types of shafts may rely on a single keyway or frictional contact, which can result in higher stress concentrations and limited load distribution.
4. Design Flexibility:
Spline shafts offer greater design flexibility compared to other types of shafts. The number, size, and shape of the splines can be customized to meet specific design requirements. This allows for optimization of torque transmission, load-bearing capacity, and relative movement characteristics based on the application’s needs. Other types of shafts may have more standardized designs and limited customization options.
5. Application Variability:
Spline shafts find widespread use in various industries and applications where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are crucial. They are commonly employed in gearboxes, power transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and other rotational systems. Other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, may be more suitable for applications that require simpler torque transmission without the need for relative movement.
6. Installation and Maintenance:
When compared to other types of shafts, spline shafts may require more precise machining and alignment during installation. The mating components must be accurately matched to ensure proper engagement and torque transfer. Additionally, spline shafts may require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure the integrity of the splines and optimal performance.
In summary, spline shafts differ from other types of shafts due to their spline structure, ability to accommodate relative movement, load distribution capability, design flexibility, application variability, and specific installation and maintenance requirements. These characteristics make spline shafts well-suited for applications that demand precise torque transmission, flexibility, and load distribution.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
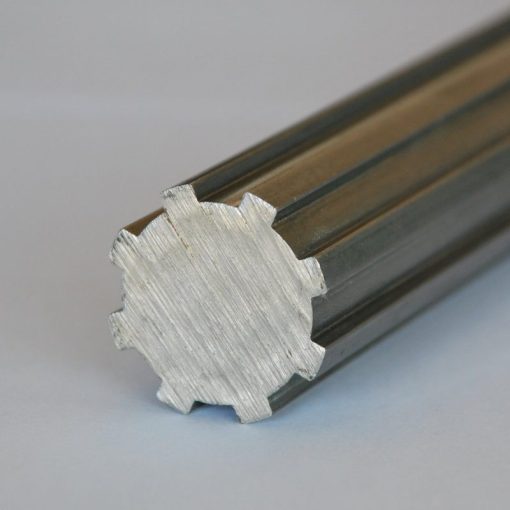
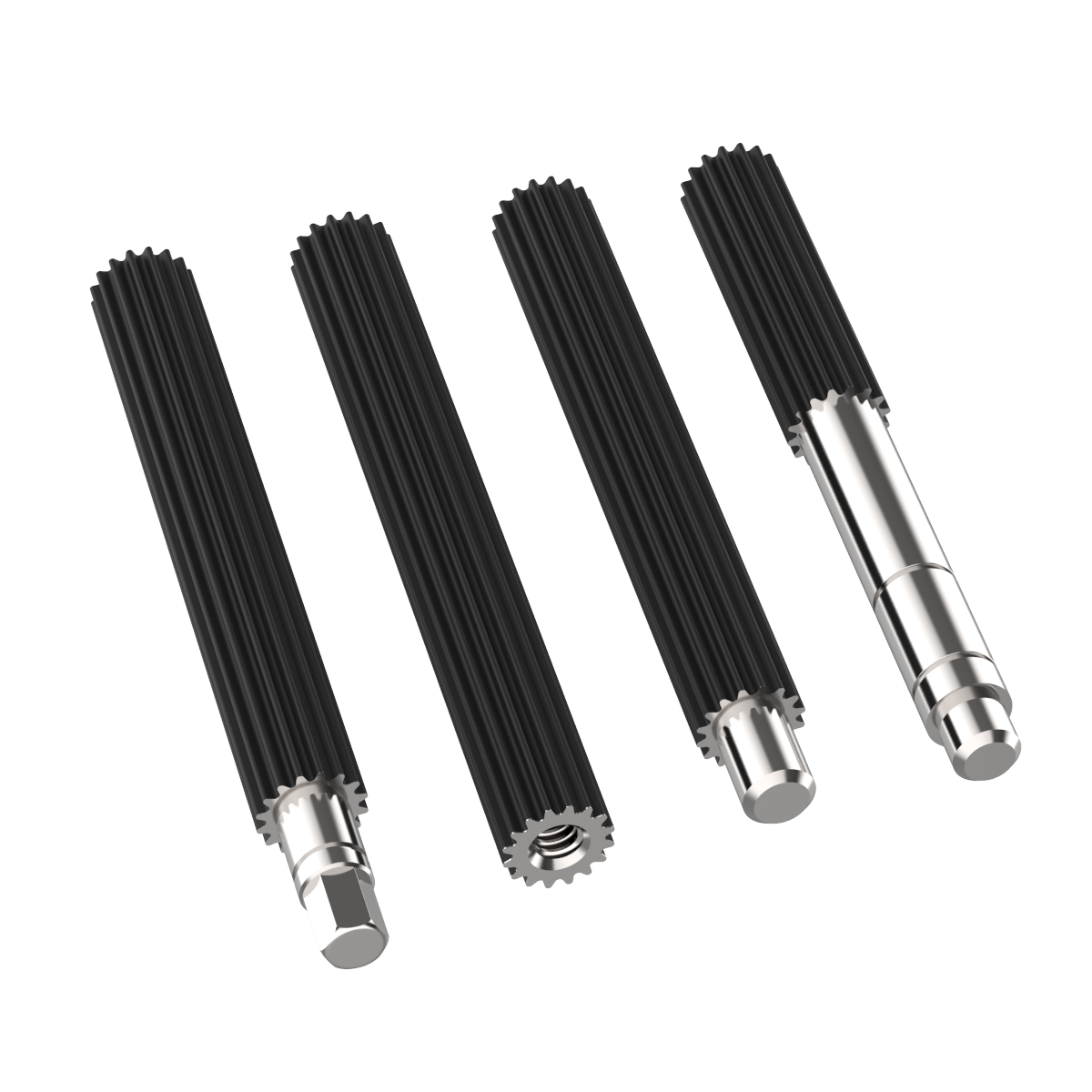
China Custom Stainless Steel CZPT Forging Spindle Spline Shaft for Spare Parts
Product Description
Forging and Machining Straight Shaft
| Material available | Carbon steel, Stainless steel, spring steel, Bronze, brass, copper alloy, aluminum alloy, tinplate, nickel silver, plastic |
| Surface treatment | Polishing\Spray Coating\Deburring\Electroplating\Oxygenation\Baking Paint\Grind\Oil CHINAMFG , etc. |
| Manufacturing Methods |
Investment Casting, Die Casting, Sand Casting, Stamping, CNC Machining, Forging, |
| Specification | OEM & Custom According to Drawing or Samples |
| Package | Standard Export Carton/According to customer’ s requirement |
Packing and Shipping
Grey Iron Housing with CHINAMFG Process
1. Standard: crate
2. Delivery: As per contract delivery on time
3. Shipping: As per client request.
Our advantages
1.We can control the products to meet your strict requirement.
2. Different kinds of finish available, like anodized, power coating, painting, polishing, electrophoresis, plating. Etc.
3. Different dimensions according to the requirements
4. Can provide various sizes and packing according to specific requirements
5. We offer the engineer consultation to your design for production improvement and cost saving
Our Service:
1.Your inquiry related to our products or prices will be replied in 24 hours.
2.Individual formula according to customers’ special drawing requests.
3.Manufacturer with large capacity, ensures the fast production cycle after
confirming the order.
4.Protection of sales area and private information for all of our customers.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Certification: | CE, GS, ISO9001 |
| Standard: | DIN, ASTM, GOST, GB, JIS, ANSI, BS |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Material: | Alloy |
| Application: | Metal Processing Machinery Parts, Metal forging Machinery |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the different types of spline profiles and their applications?
Spline profiles are used in various applications to transmit torque and motion between mating components. Here’s a detailed explanation of different spline profiles and their applications:
1. Involute Splines:
Involute splines have a trapezoidal tooth profile that allows for smooth engagement and disengagement. They are widely used in power transmission applications, such as automotive gearboxes, where high torque transmission is required. Involute splines provide excellent load distribution and can accommodate misalignment.
2. Straight Sided Splines:
Straight sided splines have straight-sided teeth that provide efficient torque transmission and high torsional stiffness. They are commonly used in applications where precise positioning is required, such as machine tools, robotics, and aerospace systems. Straight sided splines offer accurate motion control and are resistant to misalignment.
3. Serrations:
Serrations are a type of spline profile with multiple teeth in the form of parallel ridges and grooves. They are often used in applications that involve axial or linear motion, such as indexing mechanisms, clamping systems, or power tools. Serrations provide secure locking and positioning capabilities.
4. Helical Splines:
Helical splines have teeth that are helically shaped, similar to helical gears. They offer smooth and gradual tooth engagement, resulting in reduced noise and vibration. Helical splines are commonly used in applications that require high torque transmission and where quiet operation is critical, such as heavy machinery, industrial equipment, and automotive drivetrains.
5. Crowned Splines:
Crowned splines have a modified tooth profile with a slight curvature along the tooth length. This design helps distribute the load evenly across the tooth surfaces, reducing stress concentrations and improving load-carrying capacity. Crowned splines are used in applications where high load capacity and resistance to wear are essential, such as heavy-duty gearboxes, marine propulsion systems, or mining equipment.
6. Ball Splines:
Ball splines incorporate recirculating ball bearings within the spline nut and grooves on the shaft. This design enables linear motion with low friction and high precision. Ball splines are commonly used in applications that require smooth linear motion, such as CNC machines, robotics, or linear actuators.
7. Custom Splines:
In addition to the standard spline profiles mentioned above, custom spline profiles can be designed for specific applications based on unique requirements. Custom splines can be tailored to optimize torque transmission, load distribution, misalignment compensation, or other specific performance parameters.
The choice of spline profile depends on factors such as the magnitude of torque, required accuracy, misalignment tolerance, noise and vibration considerations, and environmental conditions. Engineers and designers carefully select the appropriate spline profile to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the intended application.

How do spline shafts handle variations in load capacity and weight?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in load capacity and weight in mechanical systems. Here’s how they accomplish this:
1. Material Selection:
Spline shafts are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel or alloy, chosen for their ability to withstand heavy loads and provide durability. The selection of materials takes into account factors such as tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance to ensure the shaft can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
2. Engineering Design:
Spline shafts are designed with consideration for the anticipated loads and weights they will encounter. The dimensions, profile, and number of splines are determined based on the expected torque requirements and the magnitude of the applied loads. By carefully engineering the design, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight while maintaining structural integrity and reliable performance.
3. Load Distribution:
The interlocking engagement of spline shafts allows for effective load distribution along the length of the shaft. This helps distribute the applied loads evenly, preventing localized stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of deformation or failure. By distributing the load, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight without compromising their performance.
4. Structural Reinforcement:
In applications with higher load capacities or heavier weights, spline shafts may incorporate additional structural features to enhance their strength. This can include thicker spline teeth, larger spline diameters, or reinforced sections along the shaft. By reinforcing critical areas, spline shafts can handle increased loads and weights while maintaining their integrity.
5. Lubrication and Surface Treatment:
Proper lubrication is essential for spline shafts to handle variations in load capacity and weight. Lubricants reduce friction between the mating surfaces, minimizing wear and preventing premature failure. Additionally, surface treatments such as coatings or heat treatments can enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the spline shaft, improving its ability to handle varying loads and weights.
6. Testing and Validation:
Spline shafts undergo rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet the specified load capacity and weight requirements. This may involve laboratory testing, simulation analysis, or field testing under real-world conditions. By subjecting spline shafts to thorough testing, manufacturers can verify their performance and ensure they can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
Overall, spline shafts are designed and engineered to handle variations in load capacity and weight by utilizing appropriate materials, optimizing the design, distributing loads effectively, incorporating structural reinforcement when necessary, implementing proper lubrication and surface treatments, and conducting thorough testing and validation. These measures enable spline shafts to reliably transmit torque and handle varying loads in diverse mechanical applications.

Can you explain the common applications of spline shafts in machinery?
Spline shafts have various common applications in machinery where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are essential. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Gearboxes and Transmissions:
Spline shafts are commonly used in gearboxes and transmissions where they facilitate the transmission of torque from the input shaft to the output shaft. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the gears, allowing for precise torque transfer and accommodating relative movement between the gears.
2. Power Take-Off (PTO) Units:
In agricultural and industrial machinery, spline shafts are employed in power take-off (PTO) units. PTO units allow the transfer of power from the engine to auxiliary equipment, such as pumps, generators, or farm implements. Spline shafts enable the torque transfer and accommodate the relative movement required for PTO operation.
3. Steering Systems:
Spline shafts play a crucial role in steering systems, especially in vehicles. They are used in steering columns to transmit torque from the steering wheel to the steering rack or gearbox. The splines on the shaft ensure precise torque transfer while allowing for the axial movement required for steering wheel adjustment.
4. Machine Tools:
Spline shafts find applications in machine tools such as milling machines, lathes, and grinding machines. They are used to transmit torque and enable the relative movement required for tool positioning, feed control, and spindle rotation. Spline shafts ensure accurate and controlled movement of the machine tool components.
5. Industrial Pumps and Compressors:
Spline shafts are utilized in various types of pumps and compressors, including centrifugal pumps, gear pumps, and reciprocating compressors. They transmit torque from the driver (such as an electric motor or an engine) to the impeller or rotor, enabling fluid or gas transfer. Spline shafts accommodate the axial or radial movement caused by thermal expansion or misalignment.
6. Printing and Packaging Machinery:
Spline shafts are integral components in printing and packaging machinery. They are used in processes such as web handling, where precise torque transmission and relative movement are required for tasks like tension control, registration, and material feeding. Spline shafts ensure accurate and synchronized movement of the printing and packaging elements.
7. Aerospace and Defense Systems:
In the aerospace and defense industries, spline shafts are utilized in various applications, including aircraft landing gear systems, missile guidance systems, and helicopter rotor systems. They enable torque transmission, accommodate relative movement, and ensure precise control in critical aerospace and defense mechanisms.
8. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Spline shafts are employed in construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, and loaders. They are used in hydraulic systems to transmit torque from the hydraulic motor to the driven components, such as the digger arm or the bucket. Spline shafts enable efficient power transfer and allow for the articulation and movement of the equipment.
These are just a few examples of the common applications of spline shafts in machinery. Their versatility, torque transmission capabilities, and ability to accommodate relative movement make them essential components in various industries where precise power transfer and flexibility are required.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China Best Sales Custom Precision Products High Quality Gear Shaft
Product Description
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price-quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
Inspection equipment :
Certificate:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT01-IT5 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How does the design of a spline shaft affect its performance?
The design of a spline shaft plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission:
The design of the spline shaft directly affects its ability to transmit torque efficiently. Factors such as the spline profile, number of splines, and engagement length influence the torque-carrying capacity of the shaft. A well-designed spline profile with optimized dimensions ensures maximum contact area and load distribution, resulting in improved torque transmission.
2. Load Distribution:
A properly designed spline shaft distributes the applied load evenly across the engagement surfaces. This helps to minimize stress concentrations and prevents localized wear or failure. The design should consider factors such as spline profile geometry, tooth form, and surface finish to achieve optimal load distribution and enhance the overall performance of the shaft.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
Spline shafts can accommodate a certain degree of misalignment between the mating components. The design of the spline profile can incorporate features that allow for angular or parallel misalignment, ensuring effective power transmission even under misaligned conditions. Proper design considerations help maintain smooth operation and prevent excessive stress or premature failure.
4. Torsional Stiffness:
The design of the spline shaft influences its torsional stiffness, which is the resistance to twisting under torque. A stiffer shaft design reduces torsional deflection, improves torque response, and enhances the system’s overall performance. The shaft material, diameter, and spline profile all contribute to achieving the desired torsional stiffness.
5. Fatigue Resistance:
The design of the spline shaft should consider fatigue resistance to ensure long-term durability. Fatigue failure can occur due to repeated or cyclic loading. Proper design practices, such as optimizing the spline profile, selecting appropriate materials, and incorporating suitable surface treatments, can enhance the fatigue resistance of the shaft and extend its service life.
6. Surface Finish and Lubrication:
The surface finish of the spline shaft and the lubrication used significantly impact its performance. A smooth surface finish reduces friction, wear, and the potential for corrosion. Proper lubrication ensures adequate film formation, reduces heat generation, and minimizes wear. The design should incorporate considerations for surface finish requirements and lubrication provisions to optimize the shaft’s performance.
7. Environmental Considerations:
The design should take into account the specific environmental conditions in which the spline shaft will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, exposure to chemicals, or abrasive particles can affect the shaft’s performance and longevity. Suitable material selection, surface treatments, and sealing mechanisms can be incorporated into the design to withstand the environmental challenges.
8. Manufacturing Feasibility:
The design of the spline shaft should also consider manufacturing feasibility and cost-effectiveness. Complex designs may be challenging to produce or require specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in increased production costs. Balancing design complexity with manufacturability is crucial to ensure a practical and efficient manufacturing process.
By considering these design factors, engineers can optimize the performance of spline shafts, resulting in enhanced torque transmission, improved load distribution, misalignment compensation, torsional stiffness, fatigue resistance, surface finish, and environmental compatibility. A well-designed spline shaft contributes to the overall efficiency, reliability, and longevity of the mechanical system in which it is used.

Can spline shafts be applied in aerospace and aviation equipment?
Yes, spline shafts are commonly applied in aerospace and aviation equipment due to their ability to transmit torque and provide precise rotational motion. Here’s how spline shafts are used in the aerospace and aviation industry:
1. Aircraft Engines:
Spline shafts are utilized in aircraft engines for various purposes. They can be found in the engine’s accessory gearbox, where they transmit torque from the engine to drive auxiliary components such as fuel pumps, hydraulic pumps, generators, and engine starters. Spline shafts are also present in the engine’s variable geometry systems, which control the position of components like variable stator vanes or variable inlet guide vanes.
2. Flight Control Systems:
Spline shafts play a vital role in aircraft flight control systems. They are employed in the actuators and control mechanisms that operate the flaps, ailerons, elevators, rudders, and other control surfaces. Spline shafts enable precise and efficient transfer of control inputs from the cockpit to the respective control surfaces, contributing to the maneuverability and stability of the aircraft.
3. Landing Gear:
Spline shafts are used in the landing gear systems of aircraft. They can be found in components such as the landing gear actuator, which extends and retracts the landing gear, and the steering mechanism that controls the nose wheel. Spline shafts in landing gear systems need to withstand high loads, provide reliable operation, and ensure precise movement for safe and smooth landings and takeoffs.
4. Helicopter Rotors:
Helicopters rely on spline shafts in the main rotor assembly. The main rotor shaft, which transfers power from the helicopter’s engine to the rotor blades, often incorporates splines to ensure a secure connection and efficient torque transmission. Spline shafts are critical for maintaining stable and precise rotation of the rotor blades, allowing for controlled lift and maneuverability.
5. Auxiliary Systems:
Spline shafts are also applied in various auxiliary systems in aerospace and aviation equipment. These include systems such as power transmission for onboard generators, environmental control systems, fuel control systems, and hydraulic systems. Spline shafts in these applications contribute to the reliable operation and efficient functioning of the auxiliary equipment.
In aerospace and aviation applications, spline shafts are designed to meet stringent requirements for strength, durability, precision, and weight reduction. They are often made from high-strength materials such as titanium or alloy steel to withstand the demanding operating conditions and weight constraints of aircraft. Additionally, advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to ensure the dimensional accuracy and quality of spline shafts for critical aerospace applications.
The use of spline shafts in aerospace and aviation equipment enables precise control, efficient power transmission, and reliable operation, contributing to the safety, performance, and functionality of aircraft and related systems.

In which industries are spline shafts typically used?
Spline shafts find applications in a wide range of industries where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are critical. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry extensively uses spline shafts in various components and systems. They are found in transmissions, drivelines, steering systems, differentials, and axle assemblies. Spline shafts enable the transmission of torque, accommodate relative movement, and ensure efficient power transfer in vehicles.
2. Aerospace and Defense Industry:
Spline shafts are essential in the aerospace and defense industry. They are used in aircraft landing gear systems, actuation mechanisms, missile guidance systems, engine components, and rotor assemblies. The aerospace and defense sector relies on spline shafts for precise torque transfer, relative movement accommodation, and critical control mechanisms.
3. Industrial Machinery and Equipment:
Spline shafts are widely employed in industrial machinery and equipment. They are used in gearboxes, machine tools, pumps, compressors, conveyors, printing machinery, and packaging equipment. Spline shafts enable torque transmission, accommodate misalignments and vibrations, and ensure accurate movement and synchronization of machine components.
4. Agriculture and Farming:
The agriculture and farming industry extensively uses spline shafts in equipment such as tractors, harvesters, and agricultural implements. Spline shafts are found in power take-off (PTO) units, transmission systems, hydraulic mechanisms, and steering systems. They enable torque transfer, accommodate relative movement, and provide flexibility in agricultural machinery.
5. Construction and Mining:
In the construction and mining industries, spline shafts are used in equipment such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and drilling rigs. They are found in hydraulic systems, power transmission systems, and articulated mechanisms. Spline shafts facilitate torque transmission, accommodate misalignments, and enable efficient power transfer in heavy-duty machinery.
6. Marine and Offshore:
Spline shafts have applications in the marine and offshore industry. They are used in propulsion systems, thrusters, rudders, winches, and marine pumps. Spline shafts enable torque transmission in marine vessels and offshore equipment, accommodating axial and radial movement, and ensuring reliable power transfer.
7. Energy and Power Generation:
Spline shafts are utilized in the energy and power generation sector. They are found in turbines, generators, compressors, and other rotating equipment. Spline shafts enable torque transmission and accommodate relative movement in power generation systems, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
8. Rail and Transportation:
Spline shafts are employed in the rail and transportation industry. They are found in locomotives, railcar systems, and suspension mechanisms. Spline shafts enable torque transfer, accommodate movement and vibrations, and ensure precise control in rail and transportation applications.
These are just a few examples of the industries where spline shafts are typically used. Their versatility, torque transmission capabilities, and ability to accommodate relative movement make them vital components in various sectors that rely on efficient power transfer, flexibility, and precise control.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China supplier Rotary Shaft Forged 20crmnti Forging Rotary Spline Shaft Long Roller Shaft
Product Description
CNC Precision Parts & OEM Parts Business Unit, 1 of our 3 most important business segment.
At the beginning, CNC BU was established for our own automation line spare parts demand, with our own CNC BU, our automation line can have fast and good non-standard spare parts supply, with a very good cost control.
During the last 10+ years, our CNC BU not only fulfilled our own demand, but also successfully supplied millions of non-standard spare parts according to our client’s demand.
Now with a 10+ years experienced team, highly equipped production workshop and test lab, our CNC BU grows to be a full solution precision spares supplier, we are familiar with German DIN standard, US ASTM standard, Japanese JIS standard, we can produce precision with um level in a constant quality base.
We can supply for you:
1. All kinds of Machining: Tuning, Milling, Grinding, Gear toothing, Wire cutting, Profile, Threads, and so on.
2. All kinds of Metal Materials: Carbon Steel (e.g., C45,42CrMo,16MnCr5), Stainless Steel(e.g., 303, 304, 316), Aluminum Alloy(e.g., AlCuMg2, AlSi10Mg, AlSi8Cu3, AlSi12, AlMg9, ADC12, A360, A380), Brass/Copper(e.g., ZCuZn16Si4, CuZn10, CuSn4, CuNi18Sn20), and so on.
3. All kinds of shape: Hollow Shaft, Profile Shaft, Housing, Flange, and so on.
4. All kinds of heat-treatments
5. All kinds of Coating
For more information, welcome to contact us
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Color: | Customized |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Standard: | International |
| Type: | Transmission |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
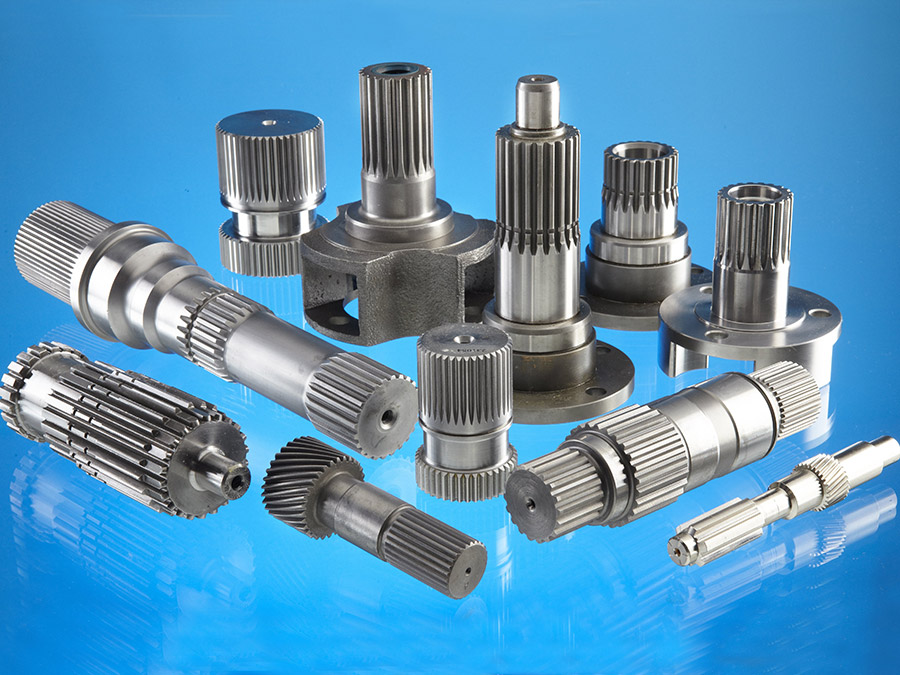

Can spline shafts be used in both mobile and stationary machinery?
Yes, spline shafts can be used in both mobile and stationary machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Mobile Machinery:
Spline shafts find extensive use in various types of mobile machinery. For example:
- In Automotive Applications: Spline shafts are commonly used in automotive drivetrains, where they transmit torque from the engine to the wheels. They are found in components such as the transmission, differential, and axle shafts.
- In Construction and Earthmoving Equipment: Spline shafts are utilized in construction machinery, such as excavators, loaders, and bulldozers. They are employed in the powertrain systems to transfer torque and drive the hydraulic pumps or propel the machine.
- In Agricultural Equipment: Spline shafts are used in agricultural machinery like tractors, combines, and harvesters. They help transfer power from the engine to various driven components, such as the wheels, PTO (power take-off), or hydraulic systems.
- In Off-Road Vehicles: Spline shafts are present in off-road vehicles, including ATVs (all-terrain vehicles) and military vehicles. They enable power transmission to the wheels or drivetrain components, ensuring mobility and performance in challenging terrains.
2. Stationary Machinery:
Spline shafts are also widely employed in stationary machinery across various industries. Some examples include:
- In Machine Tools: Spline shafts are used in machine tools, such as lathes, milling machines, and grinding machines. They provide torque transmission in the spindle or lead screw mechanisms, enabling precision motion control and material removal operations.
- In Industrial Gearboxes: Spline shafts play a crucial role in industrial gearboxes used in manufacturing and processing plants. They transmit torque between input and output shafts, enabling speed reduction or increase as required by the application.
- In Power Generation: Spline shafts are utilized in power generation equipment, including turbines and generators. They help transmit torque between the rotating rotor and the stationary components, facilitating energy conversion.
- In Pump and Compressor Systems: Spline shafts are present in pumps and compressors used in various industries. They transmit torque from the motor or prime mover to the impeller or compressor elements, enabling fluid or gas transfer.
The versatility of spline shafts makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, both mobile and stationary. Their ability to efficiently transmit torque, accommodate misalignment, distribute loads, and provide reliable connections makes them a preferred choice in diverse machinery across industries.

Can spline shafts be applied in aerospace and aviation equipment?
Yes, spline shafts are commonly applied in aerospace and aviation equipment due to their ability to transmit torque and provide precise rotational motion. Here’s how spline shafts are used in the aerospace and aviation industry:
1. Aircraft Engines:
Spline shafts are utilized in aircraft engines for various purposes. They can be found in the engine’s accessory gearbox, where they transmit torque from the engine to drive auxiliary components such as fuel pumps, hydraulic pumps, generators, and engine starters. Spline shafts are also present in the engine’s variable geometry systems, which control the position of components like variable stator vanes or variable inlet guide vanes.
2. Flight Control Systems:
Spline shafts play a vital role in aircraft flight control systems. They are employed in the actuators and control mechanisms that operate the flaps, ailerons, elevators, rudders, and other control surfaces. Spline shafts enable precise and efficient transfer of control inputs from the cockpit to the respective control surfaces, contributing to the maneuverability and stability of the aircraft.
3. Landing Gear:
Spline shafts are used in the landing gear systems of aircraft. They can be found in components such as the landing gear actuator, which extends and retracts the landing gear, and the steering mechanism that controls the nose wheel. Spline shafts in landing gear systems need to withstand high loads, provide reliable operation, and ensure precise movement for safe and smooth landings and takeoffs.
4. Helicopter Rotors:
Helicopters rely on spline shafts in the main rotor assembly. The main rotor shaft, which transfers power from the helicopter’s engine to the rotor blades, often incorporates splines to ensure a secure connection and efficient torque transmission. Spline shafts are critical for maintaining stable and precise rotation of the rotor blades, allowing for controlled lift and maneuverability.
5. Auxiliary Systems:
Spline shafts are also applied in various auxiliary systems in aerospace and aviation equipment. These include systems such as power transmission for onboard generators, environmental control systems, fuel control systems, and hydraulic systems. Spline shafts in these applications contribute to the reliable operation and efficient functioning of the auxiliary equipment.
In aerospace and aviation applications, spline shafts are designed to meet stringent requirements for strength, durability, precision, and weight reduction. They are often made from high-strength materials such as titanium or alloy steel to withstand the demanding operating conditions and weight constraints of aircraft. Additionally, advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to ensure the dimensional accuracy and quality of spline shafts for critical aerospace applications.
The use of spline shafts in aerospace and aviation equipment enables precise control, efficient power transmission, and reliable operation, contributing to the safety, performance, and functionality of aircraft and related systems.

How does a spline shaft differ from other types of shafts?
A spline shaft differs from other types of shafts in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Spline Structure:
A spline shaft features a series of ridges or teeth (splines) that are machined onto its surface. These splines create a precise and controlled interface with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. In contrast, other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, do not have the splines and rely on different mechanisms for torque transmission.
2. Torque Transmission and Relative Movement:
Unlike plain shafts or keyed shafts, which transmit torque through a frictional or mechanical connection, spline shafts allow for both torque transmission and relative movement between the shaft and mating components. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating an interlock that transfers rotational force while accommodating axial or radial displacement. This feature provides flexibility and is particularly useful in applications where misalignment or relative movement needs to be accommodated.
3. Load Distribution:
One of the advantages of spline shafts is their ability to distribute loads over a larger surface area. The multiple contact points created by the splines help distribute the applied load evenly along the shaft’s length. This load distribution minimizes stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure. In contrast, other types of shafts may rely on a single keyway or frictional contact, which can result in higher stress concentrations and limited load distribution.
4. Design Flexibility:
Spline shafts offer greater design flexibility compared to other types of shafts. The number, size, and shape of the splines can be customized to meet specific design requirements. This allows for optimization of torque transmission, load-bearing capacity, and relative movement characteristics based on the application’s needs. Other types of shafts may have more standardized designs and limited customization options.
5. Application Variability:
Spline shafts find widespread use in various industries and applications where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are crucial. They are commonly employed in gearboxes, power transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and other rotational systems. Other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, may be more suitable for applications that require simpler torque transmission without the need for relative movement.
6. Installation and Maintenance:
When compared to other types of shafts, spline shafts may require more precise machining and alignment during installation. The mating components must be accurately matched to ensure proper engagement and torque transfer. Additionally, spline shafts may require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure the integrity of the splines and optimal performance.
In summary, spline shafts differ from other types of shafts due to their spline structure, ability to accommodate relative movement, load distribution capability, design flexibility, application variability, and specific installation and maintenance requirements. These characteristics make spline shafts well-suited for applications that demand precise torque transmission, flexibility, and load distribution.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Professional Precision Transmission /Drive/Axle/Auto/Spline/Machinery Parts/ Rotor Gear Customized Machining Knurling Shaft
Product Description
Precision Shaft by CNC Turning Machining
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price-quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
Inspection equipment :
Certificate:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT01-IT5 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How does the design of a spline shaft affect its performance?
The design of a spline shaft plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission:
The design of the spline shaft directly affects its ability to transmit torque efficiently. Factors such as the spline profile, number of splines, and engagement length influence the torque-carrying capacity of the shaft. A well-designed spline profile with optimized dimensions ensures maximum contact area and load distribution, resulting in improved torque transmission.
2. Load Distribution:
A properly designed spline shaft distributes the applied load evenly across the engagement surfaces. This helps to minimize stress concentrations and prevents localized wear or failure. The design should consider factors such as spline profile geometry, tooth form, and surface finish to achieve optimal load distribution and enhance the overall performance of the shaft.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
Spline shafts can accommodate a certain degree of misalignment between the mating components. The design of the spline profile can incorporate features that allow for angular or parallel misalignment, ensuring effective power transmission even under misaligned conditions. Proper design considerations help maintain smooth operation and prevent excessive stress or premature failure.
4. Torsional Stiffness:
The design of the spline shaft influences its torsional stiffness, which is the resistance to twisting under torque. A stiffer shaft design reduces torsional deflection, improves torque response, and enhances the system’s overall performance. The shaft material, diameter, and spline profile all contribute to achieving the desired torsional stiffness.
5. Fatigue Resistance:
The design of the spline shaft should consider fatigue resistance to ensure long-term durability. Fatigue failure can occur due to repeated or cyclic loading. Proper design practices, such as optimizing the spline profile, selecting appropriate materials, and incorporating suitable surface treatments, can enhance the fatigue resistance of the shaft and extend its service life.
6. Surface Finish and Lubrication:
The surface finish of the spline shaft and the lubrication used significantly impact its performance. A smooth surface finish reduces friction, wear, and the potential for corrosion. Proper lubrication ensures adequate film formation, reduces heat generation, and minimizes wear. The design should incorporate considerations for surface finish requirements and lubrication provisions to optimize the shaft’s performance.
7. Environmental Considerations:
The design should take into account the specific environmental conditions in which the spline shaft will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, exposure to chemicals, or abrasive particles can affect the shaft’s performance and longevity. Suitable material selection, surface treatments, and sealing mechanisms can be incorporated into the design to withstand the environmental challenges.
8. Manufacturing Feasibility:
The design of the spline shaft should also consider manufacturing feasibility and cost-effectiveness. Complex designs may be challenging to produce or require specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in increased production costs. Balancing design complexity with manufacturability is crucial to ensure a practical and efficient manufacturing process.
By considering these design factors, engineers can optimize the performance of spline shafts, resulting in enhanced torque transmission, improved load distribution, misalignment compensation, torsional stiffness, fatigue resistance, surface finish, and environmental compatibility. A well-designed spline shaft contributes to the overall efficiency, reliability, and longevity of the mechanical system in which it is used.

Can spline shafts be applied in aerospace and aviation equipment?
Yes, spline shafts are commonly applied in aerospace and aviation equipment due to their ability to transmit torque and provide precise rotational motion. Here’s how spline shafts are used in the aerospace and aviation industry:
1. Aircraft Engines:
Spline shafts are utilized in aircraft engines for various purposes. They can be found in the engine’s accessory gearbox, where they transmit torque from the engine to drive auxiliary components such as fuel pumps, hydraulic pumps, generators, and engine starters. Spline shafts are also present in the engine’s variable geometry systems, which control the position of components like variable stator vanes or variable inlet guide vanes.
2. Flight Control Systems:
Spline shafts play a vital role in aircraft flight control systems. They are employed in the actuators and control mechanisms that operate the flaps, ailerons, elevators, rudders, and other control surfaces. Spline shafts enable precise and efficient transfer of control inputs from the cockpit to the respective control surfaces, contributing to the maneuverability and stability of the aircraft.
3. Landing Gear:
Spline shafts are used in the landing gear systems of aircraft. They can be found in components such as the landing gear actuator, which extends and retracts the landing gear, and the steering mechanism that controls the nose wheel. Spline shafts in landing gear systems need to withstand high loads, provide reliable operation, and ensure precise movement for safe and smooth landings and takeoffs.
4. Helicopter Rotors:
Helicopters rely on spline shafts in the main rotor assembly. The main rotor shaft, which transfers power from the helicopter’s engine to the rotor blades, often incorporates splines to ensure a secure connection and efficient torque transmission. Spline shafts are critical for maintaining stable and precise rotation of the rotor blades, allowing for controlled lift and maneuverability.
5. Auxiliary Systems:
Spline shafts are also applied in various auxiliary systems in aerospace and aviation equipment. These include systems such as power transmission for onboard generators, environmental control systems, fuel control systems, and hydraulic systems. Spline shafts in these applications contribute to the reliable operation and efficient functioning of the auxiliary equipment.
In aerospace and aviation applications, spline shafts are designed to meet stringent requirements for strength, durability, precision, and weight reduction. They are often made from high-strength materials such as titanium or alloy steel to withstand the demanding operating conditions and weight constraints of aircraft. Additionally, advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to ensure the dimensional accuracy and quality of spline shafts for critical aerospace applications.
The use of spline shafts in aerospace and aviation equipment enables precise control, efficient power transmission, and reliable operation, contributing to the safety, performance, and functionality of aircraft and related systems.

What are the advantages of using spline shafts in mechanical systems?
Using spline shafts in mechanical systems offers several advantages. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission:
Spline shafts provide efficient torque transmission between the driving and driven components. The interlocking splines ensure a secure and reliable transfer of rotational force, enabling the transmission of power and motion in mechanical systems.
2. Relative Movement Accommodation:
Spline shafts can accommodate relative movement between the driving and driven components. They allow axial, radial, and angular displacements, compensating for misalignments, thermal expansion, and vibrations. This flexibility helps to maintain proper engagement and minimize stress concentrations.
3. Load Distribution:
The splines on the shaft distribute the transmitted load across the entire engagement surface. This helps to reduce localized stresses and prevents premature wear or failure of the components. The load distribution capability of spline shafts contributes to the overall durability and longevity of the mechanical system.
4. Precise Positioning and Control:
Spline shafts enable precise positioning and control of mechanical components. The splines provide accurate rotational alignment, allowing for precise angular positioning and indexing. This is crucial in applications where precise control and synchronization of movements are required.
5. Interchangeability and Standardization:
Spline shafts are available in standardized designs and dimensions. This enables interchangeability between components and facilitates easier maintenance and replacement. Standardization also simplifies the design and manufacturing processes, reducing costs and lead times.
6. High Power Transmission Capacity:
Spline shafts are designed to withstand high torque loads. The interlocking splines provide a large contact area, distributing the transmitted torque across multiple teeth. This allows spline shafts to handle higher power transmission requirements, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
7. Versatility:
Spline shafts can be designed and manufactured to suit various application requirements. They can be customized in terms of size, shape, number of splines, and spline profile to match the specific needs of a mechanical system. This versatility makes spline shafts adaptable to a wide range of industries and applications.
8. Reduced Slippage and Backlash:
When properly designed and manufactured, spline shafts exhibit minimal slippage and backlash. The tight fit between the splines prevents significant axial or radial movement during torque transmission, resulting in improved efficiency and precision in mechanical systems.
In summary, the advantages of using spline shafts in mechanical systems include efficient torque transmission, accommodation of relative movement, load distribution, precise positioning and control, interchangeability, high power transmission capacity, versatility, and reduced slippage and backlash. These advantages make spline shafts a reliable and effective choice in various applications where power transfer, flexibility, and precise motion control are essential.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China supplier Custom Types of SWC Cardan Shaft /Universal Shaft/Spline Shaft
Product Description
Who we are?
HangZhou XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. CARDANSHAFT CO;LTD has 15 years history.When the general manager Mr.Rony Du graduated from the university,he always concentrated his attention on the research and development,production and sales of the cardan shaft.Mr.Rony Du and his team started from scratch,from 1 lathe and a very small order,step by step to grow up.He often said to his team”We will only do 1 thing well——to make the perfect cardan shaft”.
General manager Mr.Rony Du
HangZhou XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. CARDANSHAFT CO.,LTD was founded in 2005.The registered capital is 8 million ,covers an area of 15 acres, has 30 existing staff. The company specializing in the production of SWC, SWP cross universal coupling and drum tooth coupling.The company with factory is located in the beautiful coast of Tai Lake –Hudai (HangZhou Economic Development Zone Hudai Industrial Park).
In order to become China’s leading cardan shaft one-stop solution expert supplier .XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. CARDANSHAFT independent research and development of SWC light, medium, short, heavy Designs cardan shaft have reached the leading domestic level.Products not only supporting domestic large and medium-sized customers, but also exported to the United States, India, Vietnam, Laos, Ukraine, Russia, Germany, Britain and other countries and areas.In the past 15 years, the company has accumulated a wealth of experience, learn from foreign advanced technology, and to absorb and use the universal axis has been improved several times, so that the structure is maturing, significantly improved performance.
XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. Office Building
XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. belief: “Continuous innovation, optimize the structure, perseverance” to create a high quality of outstanding cardan shaft manufacturer.We always adhere to the ISO9001 quality control system, from the details to start, standardize the production process, and to achieve processing equipment “specialization, numerical control” rapid increase in product quality.This Not only won the majority of customers reputation, but also access to peer recognition. We continue to strive to pursue: “for customers to create the greatest value, for the staff to build the best platform”, will be able to achieve customer and business mutually beneficial CHINAMFG situation.
Welcome to XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. CARDANSHAFT
Why choose us?
First,select raw material carefully
The cross is the core component of cardan shaft,so the selection of material is particularly critical.Raw materials of the cross for light Duty Size and Medium Duty Size,we choose the 20CrMnTi special gear steel bar from SHAGANG GROUP.Being forged in 2500 ton friction press to ensure internal metallurgical structure,inspecting the geometric dimensions of each part to meet the drawing requirements,then transfer to machining,the processes of milling, turning, quenching and grinding.
The inspector will screen blank yoke head.The porosity, cracks, slag, etc. do not meet the requirements of the casting foundry are all eliminated,then doing physical and chemical analysis, to see whether the ingredients meet the requirements, unqualified re-elimination.And then transferred to the quenching and tempering heat treatment, once again check the hardness to see if meet the requirements, qualified to be transferred to the machining process. We control from the source of the material to ensure the supply of raw materials qualified rate of 99%.
Second,advanced production equipment
XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. Company introduced four-axis linkage machining center made in ZheJiang , milling the keyway and flange bolt hole of the flange yoke, The once machine-shaping ensures that the symmetry of the keyway and the position of the bolt hole are less than 0.02mm,which greatly improves the installation accuracy of the flange,the 4 axis milling and drilling center holes of the cross are integrated,to ensure that the 4 shaft symmetry and verticality are less than 0.02mm,the process of the journal cross assembly service life can be increased by 30%, and the speed at 1000 rpm above the cardan shaft running smoothly and super life is crucial to the operation.
We use CNC machine to lathe flange yoke and welded yoke,CNC machine can not only ensure the accuracy of the flange connection with the mouth, but also improve the flange surface finish.
5 CHINAMFG automatic welding machine welding spline sleeve and tube,welded yoke and tube.With the welding CHINAMFG swing mechanism, automatic lifting mechanism, adjustment mechanism and welding CHINAMFG cooling system, welding machine can realize multi ring continuous welding, each coil current and voltage can be preset, arc starting and stopping control PLC procedures, reliable welding quality, the weld bead is smooth and beautiful, to control the welding process with fixed procedures, greatly reducing the uncertainty of human during welding, greatly improve the welding effect.
High speed cardan shaft needs to do dynamic balance test before leaving the factory.Unbalanced cardan shaft will produce excessive centrifugal force at high speed and reduce the service life of the bearing;the dynamic balance test can eliminate the uneven distribution of the casting weight and the mass distribution of the whole assembly;Through the experiment to achieve the design of the required balance quality, improve the universal shaft service life.In 2008 the company introduced 2 high-precision dynamic balance test bench, the maximum speed can reach 4000 rev / min, the balance of G0.8 accuracy, balance weight 2kg–1000kg.
In order to make the paint standardization, in 2009 the company bought 10 CHINAMFG of clean paint room , the surface treatment of cardan shaft is more standardized, paint fastness is more rugged, staff’s working conditions improved, exhaust of harmless treatment.
Third,Professional transport packaging
The packing of the export cardan shaft is all in the same way as the plywood wooden box, and then it is firmly secured with the iron sheet, so as to avoid the damage caused by the complicated situation in the long-distance transportation. Meet the standard requirements of plywood boxes into Europe and other countries, no matter where can successfully reach all the country’s ports.
SWCZ Series-Heavy-Duty Designs Cardan shaft
Designs
Data and Size of SWCZ Series Universal Joint Couplings
| Type | Design Data Item |
SWCZ 680 |
SWCZ 700 |
SWCZ 750 |
SWCZ 780 |
SWCZ 800 |
SWCZ 840 |
SWCZ 900 |
SWCZ 920 |
SWCZ 1000 |
SWCZ 1050 |
SWCZ 1100 |
SWCZ 1200 |
| C | L | 1540 | 1600 | 1840 | 1920 | 1920 | 2120 | 2280 | 2280 | 2380 | 2480 | 2500 | 2720 |
| m(kg) | 3150 | 3450 | 4300 | 4680 | 5050 | 6400 | 8420 | 8950 | 10600 | 12100 | 13500 | 16900 | |
| D | L | 1940 | 2100 | 2400 | 2500 | 2500 | 2680 | 2950 | 2950 | 3130 | 3200 | 3300 | 3570 |
| m(kg) | 3220 | 3530 | 4500 | 5400 | 5800 | 7470 | 9980 | 10500 | 12300 | 14500 | 15800 | 19500 | |
| E | L | 3230 | 3460 | 3620 | 4000 | 4000 | 4250 | 4580 | 4850 | 4770 | 4950 | 5100 | 5660 |
| LV | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | |
| m(kg) | 4880 | 5400 | 8000 | 8450 | 9070 | 11800 | 15900 | 16500 | 19900 | 22000 | 27500 | 34800 | |
| Tn(N·m) | 1640 | 1750 | 2250 | 2500 | 2670 | 3100 | 3800 | 4050 | 5200 | 6500 | 6900 | 9000 | |
| Tf(N·m) | 980 | 1050 | 1350 | 1500 | 1600 | 1860 | 2280 | 2430 | 3120 | 3900 | 4140 | 5400 | |
| β(°) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| D | 680 | 700 | 750 | 780 | 800 | 840 | 900 | 920 | 1000 | 1060 | 1100 | 1200 | |
| Df | 680 | 700 | 750 | 780 | 800 | 840 | 900 | 920 | 1000 | 1060 | 1100 | 1200 | |
| D1 | 635 | 635 | 695 | 725 | 745 | 775 | 935 | 855 | 915 | 920 | 1015 | 1100 | |
| D2(H9) | 550 | 570 | 610 | 640 | 660 | 710 | 740 | 760 | 840 | 900 | 920 | 1000 | |
| D3 | 560 | 560 | 620 | 660 | 660 | 660 | 750 | 750 | 790 | 800 | 850 | 900 | |
| Lm | 385 | 400 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 530 | 570 | 570 | 595 | 620 | 625 | 680 | |
| k | 70 | 70 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 110 | 120 | 120 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | |
| n | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| d | 26 | 26 | 31 | 31 | 36 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 50 | 45 | 50 | 58 | |
| Flange bolt | M24 | M24 | M30 | M30 | M30 | M36 | M36 | M36 | M48 | M42 | M48 | M56 |
1. Notations:
L=Standard length, or compressed length for designs with length compensation;
LV=Length compensation;
M=Weight;
Tn=Nominal torque(Yield torque 50% over Tn);
TF=Fatigue torque, I. E. Permissible torque as determined according to the fatigue strength
Under reversing loads;
β=Maximum deflection angle;
MI=weight per 100mm tube
2. Millimeters are used as measurement units except where noted;
3. Please consult us for customizations regarding length, length compensation and
Flange connections.
(DIN or SAT etc. )
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Hollow Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What safety considerations should be kept in mind when working with spline shafts?
Working with spline shafts requires adherence to certain safety considerations to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the machinery or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
When working with spline shafts, individuals should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with lubricants.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Prior to performing any maintenance or repair work on machinery or equipment involving spline shafts, proper lockout/tagout procedures should be followed. This involves isolating the power source, de-energizing the system, and securing it with lockout devices or tags to prevent accidental startup or release of stored energy.
3. Training and Competence:
Only trained and competent personnel should work with spline shafts. They should have a thorough understanding of the machinery or equipment, including the operation, maintenance, and safety procedures specific to spline shafts. Adequate training and knowledge help minimize the risk of accidents or improper handling.
4. Proper Handling and Lifting Techniques:
When moving or lifting machinery components that include spline shafts, proper techniques should be employed. This includes using appropriate lifting equipment, maintaining a stable posture, and avoiding sudden movements that could cause strain or injury.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Spline shafts should be regularly inspected for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Any abnormalities should be addressed promptly by qualified personnel. Routine maintenance, such as lubrication and cleaning, should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
6. Correct Installation and Alignment:
During installation or replacement of spline shafts, proper alignment and fit should be ensured. The shafts should be correctly seated and engaged with the mating components, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Improper installation or misalignment can lead to premature wear, excessive stress, or failure of the spline shafts.
7. Hazardous Environments:
When spline shafts are used in hazardous environments, such as those with flammable substances, extreme temperatures, or high vibrations, additional safety measures may be required. These may include explosion-proof enclosures, temperature monitoring, or vibration damping systems.
8. Emergency Procedures:
Emergency procedures should be established and communicated to all personnel working with spline shafts. This includes knowing the location of emergency stops, emergency shutdown procedures, and the contact information for emergency response personnel.
9. Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations regarding the installation, operation, and maintenance of spline shafts. The manufacturer’s instructions provide specific safety information and precautions tailored to their product.
By taking these safety considerations into account and implementing appropriate measures, the risks associated with working with spline shafts can be minimized. Safety should always be a top priority when dealing with machinery or equipment that incorporates spline shafts.

Can spline shafts be applied in aerospace and aviation equipment?
Yes, spline shafts are commonly applied in aerospace and aviation equipment due to their ability to transmit torque and provide precise rotational motion. Here’s how spline shafts are used in the aerospace and aviation industry:
1. Aircraft Engines:
Spline shafts are utilized in aircraft engines for various purposes. They can be found in the engine’s accessory gearbox, where they transmit torque from the engine to drive auxiliary components such as fuel pumps, hydraulic pumps, generators, and engine starters. Spline shafts are also present in the engine’s variable geometry systems, which control the position of components like variable stator vanes or variable inlet guide vanes.
2. Flight Control Systems:
Spline shafts play a vital role in aircraft flight control systems. They are employed in the actuators and control mechanisms that operate the flaps, ailerons, elevators, rudders, and other control surfaces. Spline shafts enable precise and efficient transfer of control inputs from the cockpit to the respective control surfaces, contributing to the maneuverability and stability of the aircraft.
3. Landing Gear:
Spline shafts are used in the landing gear systems of aircraft. They can be found in components such as the landing gear actuator, which extends and retracts the landing gear, and the steering mechanism that controls the nose wheel. Spline shafts in landing gear systems need to withstand high loads, provide reliable operation, and ensure precise movement for safe and smooth landings and takeoffs.
4. Helicopter Rotors:
Helicopters rely on spline shafts in the main rotor assembly. The main rotor shaft, which transfers power from the helicopter’s engine to the rotor blades, often incorporates splines to ensure a secure connection and efficient torque transmission. Spline shafts are critical for maintaining stable and precise rotation of the rotor blades, allowing for controlled lift and maneuverability.
5. Auxiliary Systems:
Spline shafts are also applied in various auxiliary systems in aerospace and aviation equipment. These include systems such as power transmission for onboard generators, environmental control systems, fuel control systems, and hydraulic systems. Spline shafts in these applications contribute to the reliable operation and efficient functioning of the auxiliary equipment.
In aerospace and aviation applications, spline shafts are designed to meet stringent requirements for strength, durability, precision, and weight reduction. They are often made from high-strength materials such as titanium or alloy steel to withstand the demanding operating conditions and weight constraints of aircraft. Additionally, advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to ensure the dimensional accuracy and quality of spline shafts for critical aerospace applications.
The use of spline shafts in aerospace and aviation equipment enables precise control, efficient power transmission, and reliable operation, contributing to the safety, performance, and functionality of aircraft and related systems.

How does a spline shaft differ from other types of shafts?
A spline shaft differs from other types of shafts in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Spline Structure:
A spline shaft features a series of ridges or teeth (splines) that are machined onto its surface. These splines create a precise and controlled interface with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. In contrast, other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, do not have the splines and rely on different mechanisms for torque transmission.
2. Torque Transmission and Relative Movement:
Unlike plain shafts or keyed shafts, which transmit torque through a frictional or mechanical connection, spline shafts allow for both torque transmission and relative movement between the shaft and mating components. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating an interlock that transfers rotational force while accommodating axial or radial displacement. This feature provides flexibility and is particularly useful in applications where misalignment or relative movement needs to be accommodated.
3. Load Distribution:
One of the advantages of spline shafts is their ability to distribute loads over a larger surface area. The multiple contact points created by the splines help distribute the applied load evenly along the shaft’s length. This load distribution minimizes stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure. In contrast, other types of shafts may rely on a single keyway or frictional contact, which can result in higher stress concentrations and limited load distribution.
4. Design Flexibility:
Spline shafts offer greater design flexibility compared to other types of shafts. The number, size, and shape of the splines can be customized to meet specific design requirements. This allows for optimization of torque transmission, load-bearing capacity, and relative movement characteristics based on the application’s needs. Other types of shafts may have more standardized designs and limited customization options.
5. Application Variability:
Spline shafts find widespread use in various industries and applications where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are crucial. They are commonly employed in gearboxes, power transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and other rotational systems. Other types of shafts, such as plain shafts or keyed shafts, may be more suitable for applications that require simpler torque transmission without the need for relative movement.
6. Installation and Maintenance:
When compared to other types of shafts, spline shafts may require more precise machining and alignment during installation. The mating components must be accurately matched to ensure proper engagement and torque transfer. Additionally, spline shafts may require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure the integrity of the splines and optimal performance.
In summary, spline shafts differ from other types of shafts due to their spline structure, ability to accommodate relative movement, load distribution capability, design flexibility, application variability, and specific installation and maintenance requirements. These characteristics make spline shafts well-suited for applications that demand precise torque transmission, flexibility, and load distribution.


editor by CX 2024-05-13
China wholesaler China Factory High Precision Spline Motor Shaft
Product Description
1.Product Descrition: China Factory High Precision Spline Motor Shaft
Material (Blank blanking) – (Medium frequency hardening) frequency CHINAMFG – hole (Pier hole) – pier (Rough CNC) – rough semi refined car (Half finished CNC) – rolling, rolling lines (Knurling, Rolled thread) – (Milling flutes) – milling heat treatment (Heat treatment) – (coarse and fine grinding each one) Mill (Coarse and fine) – cleaning, packaging and warehousing (Cleaning and packing)
2.Product Details;
| Core competence | drive shaft,pump shaft, motor shaft,rotor shaft ,blender shaft and multi -diameter shaft etc precision shaft core. |
| Surface Treament | Anodizing/ Oxiding/ Zinc plating/ Nickel plating/ Chrome plating/ Silver plating/ Gold plating/ Imitation gold plating/ Sand blasted/ Brushed/ Silk screen/ Passivation/ Power coating/ Painting/ Alodine/ Heat treatment/ Teflon etc. |
| Tolerance | +/-0.005mm or +/- 0.0002″ |
| Material | Stainless Steel,Carbon Steel |
| We handle many other type of materials. Please contact us if your required material is not listed above. | |
| Inspecation Equipment | Coordinate measuring machining/ Projector/ Caliper/ Microscope/ Micrometer/ High gauge/ Roughness tester/ Gauge block/ Thread gauge etc. |
| Quality Control | 100% inspection |
| Customized | Yes,all are customized according clients’ drawings design or sample |
| Payment Way | T/T, Western Union ,Paypal |
| Packaging | 1:Anti-rust oil OPP bags and cartons for outer packages. |
| 2: Customer’s requirement. | |
| Shipping | (1)0-100kg: express & air freight priority |
| (2)>100kg: sea freight priority | |
| (3)As per customized specifications. |
3.Products processing:
FAQ:
1.Can we get a sample before ordering?
Sure,sample is free,you have to pay freight cost or supply us your company collect couire account number.tks
2.All products all are OEM ?
Yes,our specialized in producing and exporting various shafts and pin,all are high quality and customized according to clients’ drawings or samples.
3.Are you factory or a trading company ?
We are manuacturer,and our factory is in HangZhou,china.
welcome to visit us anytime.
4.Why choose us?
Because we can help you produce high quanlity and Precision shaft according to your design drawing.
welcome to OEM products anytime.
Sure,competive price and good delivery time service
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | OEM |
| Axis Shape: | OEM |
| Shaft Shape: | OEM |
| Samples: |
US$ 9.99/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do spline shafts handle variations in torque and rotational force?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in torque and rotational force in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Interlocking Splines:
Spline shafts have a series of interlocking splines along their length. These splines engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, such as gears or couplings. The interlocking design ensures a secure and robust connection, capable of transmitting torque and rotational force.
2. Load Distribution:
When torque is applied to a spline shaft, the load is distributed across the entire engagement surface of the splines. This helps to minimize stress concentrations and prevents localized wear or failure. The load distribution capability of spline shafts allows them to handle variations in torque and rotational force effectively.
3. Material Selection:
Spline shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and durability, such as alloy steels. The material selection is crucial in handling variations in torque and rotational force. It ensures that the spline shaft can withstand the applied loads without deformation or failure.
4. Spline Profile:
The design of the spline profile also contributes to the handling of torque variations. The spline profile determines the contact area and the distribution of forces along the splines. By optimizing the spline profile, manufacturers can enhance the load-carrying capacity and improve the ability of the spline shaft to handle variations in torque.
5. Surface Finish and Lubrication:
Proper surface finish and lubrication play a crucial role in the performance of spline shafts. A smooth surface finish reduces friction and wear, while suitable lubrication minimizes heat generation and ensures smooth operation. These factors help in handling variations in torque and rotational force by reducing the impact of friction and wear on the spline engagement.
6. Design Considerations:
Engineers take several design considerations into account to ensure spline shafts can handle variations in torque and rotational force. These considerations include appropriate spline dimensions, tooth profile geometry, spline fit tolerance, and the selection of mating components. By carefully designing the spline shaft and its mating components, engineers can optimize the system’s performance and reliability.
7. Overload Protection:
In some applications, spline shafts may be equipped with overload protection mechanisms. These mechanisms, such as shear pins or torque limiters, are designed to disconnect the drive temporarily or slip when the torque exceeds a certain threshold. This protects the spline shaft and other components from damage due to excessive torque.
Overall, spline shafts handle variations in torque and rotational force through their interlocking splines, load distribution capability, appropriate material selection, optimized spline profiles, surface finish, lubrication, design considerations, and, in some cases, overload protection mechanisms. These features ensure efficient torque transmission and enable spline shafts to withstand the demands of various mechanical systems.

Can spline shafts be repaired or maintained when necessary?
Yes, spline shafts can be repaired and maintained when necessary to ensure their continued functionality and performance. Here are some ways spline shafts can be repaired and maintained:
1. Inspection and Assessment:
When an issue is suspected with a spline shaft, the first step is to conduct a thorough inspection. This involves examining the shaft for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Special attention is given to the spline teeth, which may show signs of wear or deformation. Through inspection and assessment, the extent of the repair or maintenance required can be determined.
2. Spline Tooth Repair:
If the spline teeth are damaged or worn, they can be repaired or replaced. Repair methods may include re-machining the teeth to restore their original profile, filling and reshaping the worn areas using specialized welding techniques, or replacing the damaged section of the spline shaft. The specific repair method depends on the severity of the damage and the material of the spline shaft.
3. Lubrication and Cleaning:
Regular lubrication and cleaning are essential for maintaining spline shafts. Lubricants help reduce friction and wear between the mating surfaces, while cleaning removes contaminants that can affect the spline’s engagement. During maintenance, old lubricants are removed, and fresh lubricants are applied to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature failure.
4. Surface Treatment:
If the spline shaft undergoes wear or corrosion, surface treatment can be applied to restore its condition. This may involve applying coatings or treatments to enhance the hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion resistance of the spline shaft. Surface treatments can improve the longevity and performance of the spline shaft, reducing the need for frequent repairs.
5. Balancing and Alignment:
If a spline shaft is experiencing vibration or misalignment issues, it may require balancing or realignment. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the shaft to minimize vibrations, while alignment ensures proper mating and engagement with other components. Balancing and alignment procedures help optimize the performance and longevity of the spline shaft.
6. Replacement:
In cases where the spline shaft is severely damaged or worn beyond repair, replacement may be necessary. Replacement spline shafts can be sourced from manufacturers or specialized suppliers who can provide shafts that meet the required specifications and tolerances.
It’s important to note that the repair and maintenance of spline shafts should be carried out by qualified professionals with expertise in precision machining and mechanical systems. They have the knowledge and tools to properly assess, repair, or replace spline shafts, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the system in which they are used.
By implementing regular maintenance and timely repairs, spline shafts can be kept in optimal condition, extending their lifespan and maintaining their performance in various mechanical applications.

What are the key components and design features of a spline shaft?
A spline shaft consists of several key components and incorporates specific design features to ensure its functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Shaft Body:
The main component of a spline shaft is the shaft body, which provides the structural integrity and serves as the base for the spline features. The shaft body is typically cylindrical in shape and made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, or other alloyed metals. The material selection depends on factors like the application requirements, torque loads, and environmental conditions.
2. Splines:
The splines are the key design feature of a spline shaft. They are ridges or teeth that are machined onto the surface of the shaft. The splines create the interlocking mechanism with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. The number, size, and shape of the splines can vary depending on the application requirements and design specifications.
3. Spline Profile:
The spline profile refers to the specific shape or geometry of the splines. Common types of spline profiles include involute, straight-sided, and serrated. The spline profile is chosen based on factors such as the torque transmission requirements, load distribution, and the desired engagement characteristics with mating components. The spline profile ensures optimal contact and torque transfer between the spline shaft and the mating component.
4. Spline Fit:
The spline fit refers to the dimensional relationship between the spline shaft and the mating component. It determines the clearance or interference between the splines, ensuring proper engagement and transmission of torque. The spline fit can be categorized into different classes, such as clearance fit, transition fit, or interference fit, based on the desired level of clearance or interference.
5. Surface Finish:
The surface finish of the spline shaft is crucial for its performance. The splines and the shaft body should have a smooth and consistent surface finish to minimize friction, wear, and the risk of stress concentrations. The surface finish can be achieved through machining, grinding, or other surface treatment methods to meet the required specifications.
6. Lubrication:
To ensure smooth operation and reduce wear, lubrication is often employed for spline shafts. Lubricants with appropriate viscosity and lubricating properties are applied to the spline interface to minimize friction, dissipate heat, and prevent premature wear or damage to the splines and mating components. Lubrication also helps in maintaining the functionality and prolonging the service life of the spline shaft.
7. Machining Tolerances:
Precision machining is critical for spline shafts to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and ensure proper engagement with mating components. Tight machining tolerances are maintained during the manufacturing process to ensure the spline profile, dimensions, and surface finish meet the specified design requirements. This ensures the interchangeability and compatibility of spline shafts in various applications.
In summary, the key components and design features of a spline shaft include the shaft body, splines, spline profile, spline fit, surface finish, lubrication, and machining tolerances. These elements work together to enable torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution while ensuring the functionality, durability, and performance of the spline shaft.


editor by CX 2024-05-10