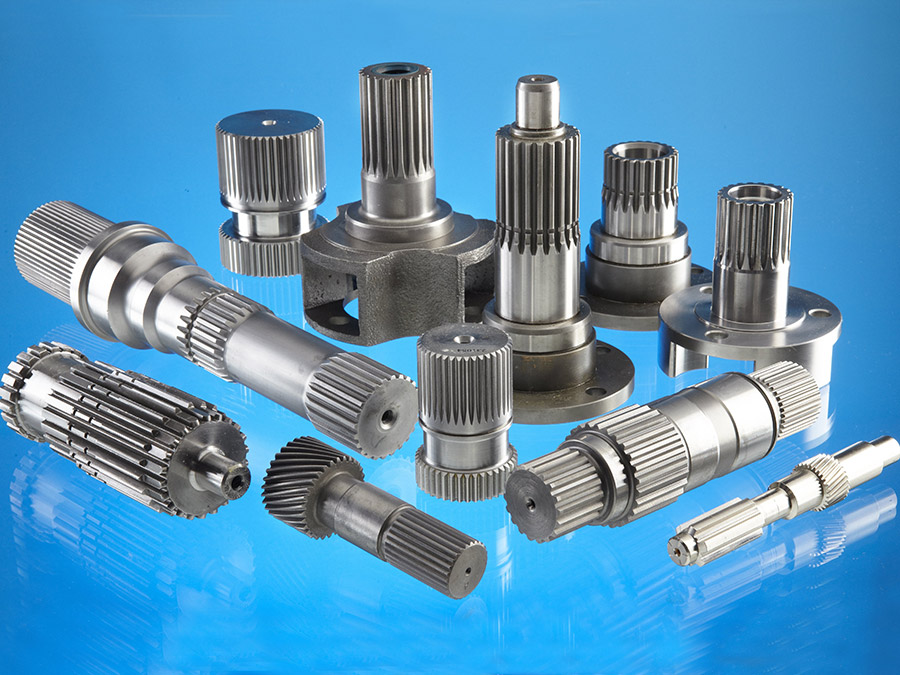
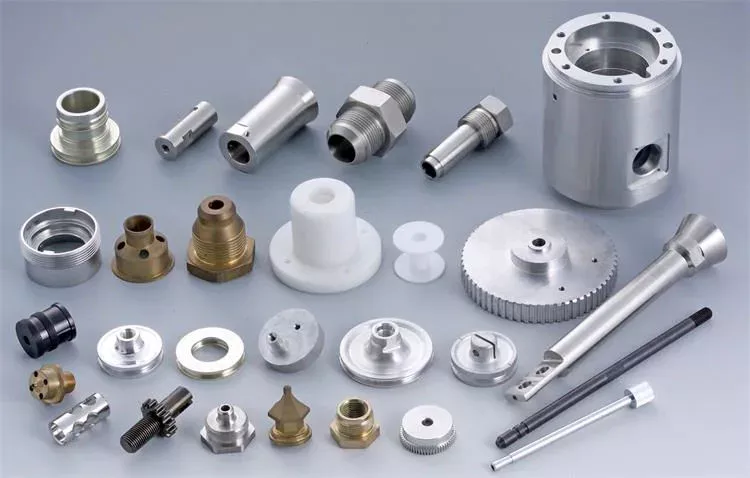
Product Description
Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20CrMoTi
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
(2) Forged with 42CrMo material and heat treated and tempered for 32 degrees, so that the half shaft has stronger toughness and is not easy to break and bend.
(3) Processed in the machining center, ensure that the products have rigorous dimensional coordinates to ensure 100% qualified rate of products.
(4) Products are inspected 1 by 1 and delivered out of the warehouse, with unified laser identification to ensure product traceability.
(5) Various sizes of axle shafts can be customized to meet customer needs.
(6) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
Factory Show
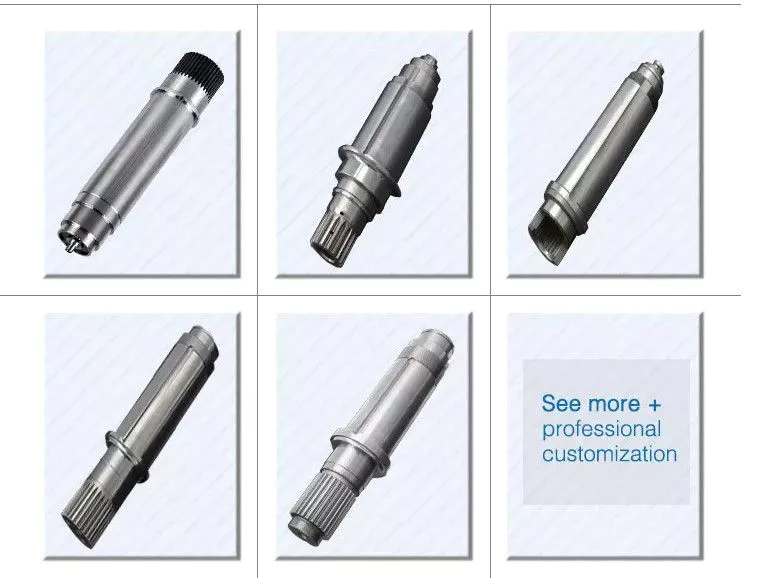
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, CHINAMFG Auman, CHINAMFG Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Liuqi Balong, North BENZ( BEIBEN), C&C, JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Function
Heavy trucks usually have double rear axles. If they are driven separately, they need to use 2 transmission shafts or add a transfer case at the output of the gearbox, which is heavy and cumbersome. Now a through shaft is designed in the middle axle to solve this problem. Only 1 transmission shaft is needed to drive 2 rear axles at the same time.
Packaging & Shipping
Exhibition
FAQ
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
We are a factory integrating research, development, production and sales.
Q2. What are the advantages of your products?
We support product customization to meet customer needs for special products. We can strictly control the products from raw materials to production, processing, product quality inspection, delivery, packaging, etc., and provide customers with high-end products and the most advantageous prices.
Q3. How about products price?
We are a factory, all products are direct sale at factory price. For the same price, we will provide the best quality; for the same quality, we have the most advantageous price.
Q4. What is your terms of packing?
We have branded packaging and neutral packaging, and we can also do what you want with authorization. This is flexible.
Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Certifications
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | 45#Steel, 42CrMo, 20crmoti |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | High Precision |
| Samples: |
US$ 29/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can spline shafts be used in both mobile and stationary machinery?
Yes, spline shafts can be used in both mobile and stationary machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Mobile Machinery:
Spline shafts find extensive use in various types of mobile machinery. For example:
- In Automotive Applications: Spline shafts are commonly used in automotive drivetrains, where they transmit torque from the engine to the wheels. They are found in components such as the transmission, differential, and axle shafts.
- In Construction and Earthmoving Equipment: Spline shafts are utilized in construction machinery, such as excavators, loaders, and bulldozers. They are employed in the powertrain systems to transfer torque and drive the hydraulic pumps or propel the machine.
- In Agricultural Equipment: Spline shafts are used in agricultural machinery like tractors, combines, and harvesters. They help transfer power from the engine to various driven components, such as the wheels, PTO (power take-off), or hydraulic systems.
- In Off-Road Vehicles: Spline shafts are present in off-road vehicles, including ATVs (all-terrain vehicles) and military vehicles. They enable power transmission to the wheels or drivetrain components, ensuring mobility and performance in challenging terrains.
2. Stationary Machinery:
Spline shafts are also widely employed in stationary machinery across various industries. Some examples include:
- In Machine Tools: Spline shafts are used in machine tools, such as lathes, milling machines, and grinding machines. They provide torque transmission in the spindle or lead screw mechanisms, enabling precision motion control and material removal operations.
- In Industrial Gearboxes: Spline shafts play a crucial role in industrial gearboxes used in manufacturing and processing plants. They transmit torque between input and output shafts, enabling speed reduction or increase as required by the application.
- In Power Generation: Spline shafts are utilized in power generation equipment, including turbines and generators. They help transmit torque between the rotating rotor and the stationary components, facilitating energy conversion.
- In Pump and Compressor Systems: Spline shafts are present in pumps and compressors used in various industries. They transmit torque from the motor or prime mover to the impeller or compressor elements, enabling fluid or gas transfer.
The versatility of spline shafts makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, both mobile and stationary. Their ability to efficiently transmit torque, accommodate misalignment, distribute loads, and provide reliable connections makes them a preferred choice in diverse machinery across industries.

How do spline shafts contribute to precise and consistent rotation?
Spline shafts play a crucial role in achieving precise and consistent rotation in mechanical systems. Here’s how spline shafts contribute to these characteristics:
1. Interlocking Design:
Spline shafts feature a series of ridges or teeth, known as splines, that interlock with corresponding grooves or slots in mating components. This interlocking design ensures a positive connection between the shaft and the mating part, allowing for precise and consistent rotation. The engagement between the splines provides resistance to axial and radial movement, minimizing play or backlash that can introduce inaccuracies in rotation.
2. Load Distribution:
The interlocking engagement of spline shafts allows for effective load distribution along the length of the shaft. This helps distribute the applied torque evenly, reducing stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of localized deformation or failure. By distributing the load, spline shafts contribute to consistent rotation and prevent excessive wear on specific areas of the shaft or the mating components.
3. Torque Transmission:
Spline shafts are specifically designed to transmit torque efficiently from one component to another. The close fit between the splines ensures a high torque-carrying capacity, enabling the shaft to transfer rotational force without significant power loss. This efficient torque transmission contributes to precise and consistent rotation, allowing for accurate positioning and motion control in various applications.
4. Rigidity and Stiffness:
Spline shafts are typically constructed from materials with high rigidity and stiffness, such as steel or alloy. This inherent rigidity helps maintain the dimensional integrity of the shaft and minimizes deflection or bending under load. By providing a stable and stiff rotational axis, spline shafts contribute to precise and consistent rotation, particularly in applications that require tight tolerances or high-speed operation.
5. Alignment and Centering:
The interlocking nature of spline shafts aids in the alignment and centering of rotating components. The splines ensure proper positioning and orientation of the shaft relative to the mating part, facilitating concentric rotation. This alignment helps prevent wobbling, vibrations, and eccentricity, which can adversely affect rotation accuracy and consistency.
6. Lubrication and Wear Reduction:
Proper lubrication of spline shafts is essential for maintaining precise and consistent rotation. Lubricants reduce friction between the mating surfaces, minimizing wear and preventing stick-slip phenomena that can cause irregular rotation. The use of lubrication also helps dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the spline shaft.
By incorporating interlocking design, load distribution, efficient torque transmission, rigidity, alignment, and lubrication, spline shafts contribute to precise and consistent rotation in mechanical systems. Their reliable and accurate rotational characteristics make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive and aerospace to machinery and robotics.

In which industries are spline shafts typically used?
Spline shafts find applications in a wide range of industries where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are critical. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry extensively uses spline shafts in various components and systems. They are found in transmissions, drivelines, steering systems, differentials, and axle assemblies. Spline shafts enable the transmission of torque, accommodate relative movement, and ensure efficient power transfer in vehicles.
2. Aerospace and Defense Industry:
Spline shafts are essential in the aerospace and defense industry. They are used in aircraft landing gear systems, actuation mechanisms, missile guidance systems, engine components, and rotor assemblies. The aerospace and defense sector relies on spline shafts for precise torque transfer, relative movement accommodation, and critical control mechanisms.
3. Industrial Machinery and Equipment:
Spline shafts are widely employed in industrial machinery and equipment. They are used in gearboxes, machine tools, pumps, compressors, conveyors, printing machinery, and packaging equipment. Spline shafts enable torque transmission, accommodate misalignments and vibrations, and ensure accurate movement and synchronization of machine components.
4. Agriculture and Farming:
The agriculture and farming industry extensively uses spline shafts in equipment such as tractors, harvesters, and agricultural implements. Spline shafts are found in power take-off (PTO) units, transmission systems, hydraulic mechanisms, and steering systems. They enable torque transfer, accommodate relative movement, and provide flexibility in agricultural machinery.
5. Construction and Mining:
In the construction and mining industries, spline shafts are used in equipment such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and drilling rigs. They are found in hydraulic systems, power transmission systems, and articulated mechanisms. Spline shafts facilitate torque transmission, accommodate misalignments, and enable efficient power transfer in heavy-duty machinery.
6. Marine and Offshore:
Spline shafts have applications in the marine and offshore industry. They are used in propulsion systems, thrusters, rudders, winches, and marine pumps. Spline shafts enable torque transmission in marine vessels and offshore equipment, accommodating axial and radial movement, and ensuring reliable power transfer.
7. Energy and Power Generation:
Spline shafts are utilized in the energy and power generation sector. They are found in turbines, generators, compressors, and other rotating equipment. Spline shafts enable torque transmission and accommodate relative movement in power generation systems, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
8. Rail and Transportation:
Spline shafts are employed in the rail and transportation industry. They are found in locomotives, railcar systems, and suspension mechanisms. Spline shafts enable torque transfer, accommodate movement and vibrations, and ensure precise control in rail and transportation applications.
These are just a few examples of the industries where spline shafts are typically used. Their versatility, torque transmission capabilities, and ability to accommodate relative movement make them vital components in various sectors that rely on efficient power transfer, flexibility, and precise control.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China Hot selling Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20crmoti
Product Description
Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20CrMoTi
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
(2) Forged with 42CrMo material and heat treated and tempered for 32 degrees, so that the half shaft has stronger toughness and is not easy to break and bend.
(3) Processed in the machining center, ensure that the products have rigorous dimensional coordinates to ensure 100% qualified rate of products.
(4) Products are inspected 1 by 1 and delivered out of the warehouse, with unified laser identification to ensure product traceability.
(5) Various sizes of axle shafts can be customized to meet customer needs.
(6) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
Factory Show
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, CHINAMFG Auman, CHINAMFG Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Liuqi Balong, North BENZ( BEIBEN), C&C, JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Function
Heavy trucks usually have double rear axles. If they are driven separately, they need to use 2 transmission shafts or add a transfer case at the output of the gearbox, which is heavy and cumbersome. Now a through shaft is designed in the middle axle to solve this problem. Only 1 transmission shaft is needed to drive 2 rear axles at the same time.
Packaging & Shipping
Exhibition
FAQ
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
We are a factory integrating research, development, production and sales.
Q2. What are the advantages of your products?
We support product customization to meet customer needs for special products. We can strictly control the products from raw materials to production, processing, product quality inspection, delivery, packaging, etc., and provide customers with high-end products and the most advantageous prices.
Q3. How about products price?
We are a factory, all products are direct sale at factory price. For the same price, we will provide the best quality; for the same quality, we have the most advantageous price.
Q4. What is your terms of packing?
We have branded packaging and neutral packaging, and we can also do what you want with authorization. This is flexible.
Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Certifications
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | 45#Steel, 42CrMo, 20crmoti |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | High Precision |
| Samples: |
US$ 29/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do spline shafts contribute to efficient power transmission?
Spline shafts play a vital role in enabling efficient power transmission in various mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how spline shafts contribute to efficient power transmission:
1. Torque Transmission:
Spline shafts are designed to transmit torque from one component to another. They provide a positive, non-slip connection that allows for efficient power transfer without slippage or loss of energy. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating a strong mechanical connection for torque transmission.
2. Load Distribution:
Spline shafts distribute the applied load evenly across the engagement surfaces. The teeth or grooves on the shaft’s spline profile ensure that the load is shared across multiple contact points. This even load distribution helps prevent localized stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure. Efficient load distribution ensures that power is transmitted smoothly and reliably.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
Spline shafts can accommodate a certain degree of misalignment between the mating components. The spline profile design allows for angular or parallel misalignment without compromising the power transmission capability. This misalignment compensation capability is crucial in maintaining efficient power transmission in situations where perfect alignment is challenging or subject to variations.
4. High Torque Capacity:
Spline shafts are designed to withstand high torque levels. The spline profile, engagement length, and material selection are optimized to handle the expected torque requirements. This high torque capacity ensures that the shaft can efficiently transmit power without experiencing excessive deflection or failure under normal operating conditions.
5. Torsional Stiffness:
Spline shafts exhibit high torsional stiffness, which means they resist twisting or torsional deflection when subjected to torque. The shaft’s design, including its diameter, spline profile, and material properties, contributes to its torsional stiffness. High torsional stiffness minimizes power loss due to deformation or flexing of the shaft, allowing for efficient power transmission.
6. Reliable Connection:
Spline shafts provide a reliable and repeatable connection between the driving and driven components. Once properly engaged, the spline shaft maintains its connection, ensuring consistent power transmission over time. This reliability is crucial in maintaining efficiency and preventing power loss or interruptions during operation.
7. Minimal Backlash:
Backlash refers to the slight rotational play or clearance between mating components. Spline shafts, when properly designed and manufactured, can minimize backlash in the power transmission system. Reduced backlash ensures smoother operation, improved accuracy, and efficiency by minimizing power losses associated with reversing or changing direction.
8. Compact Design:
Spline shafts offer a compact and space-efficient solution for power transmission. Their design allows for a relatively small footprint while providing robust torque transmission capabilities. The compact design is particularly advantageous in applications where space is limited, such as automotive drivetrains or compact machinery.
By incorporating spline shafts into mechanical systems, engineers can achieve efficient power transmission, ensuring that power is effectively transferred from the driving source to the driven components. The unique design features of spline shafts enable reliable torque transmission, even load distribution, misalignment compensation, high torque capacity, torsional stiffness, reliable connections, minimal backlash, and compactness.

How do spline shafts handle variations in environmental conditions?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in environmental conditions and maintain their performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Temperature Variations:
Spline shafts are engineered to withstand a wide range of temperature variations. They are constructed from materials that exhibit good thermal stability, such as high-grade steels or alloys. These materials have low coefficients of thermal expansion, minimizing the effects of temperature changes on the shaft’s dimensional stability. Additionally, proper lubrication with temperature-resistant lubricants helps reduce friction and wear in the spline engagement, even under extreme temperature conditions.
2. Moisture and Corrosion Resistance:
Spline shafts can be designed to resist moisture and corrosion, ensuring their performance in humid or corrosive environments. Protective coatings, such as platings or surface treatments, can be applied to the shaft’s surfaces to enhance their resistance to moisture, oxidation, and corrosion. Additionally, selecting materials with inherent corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys, can further enhance the spline shaft’s ability to handle environmental conditions.
3. Dust and Contaminant Protection:
Spline shafts used in environments with high levels of dust, dirt, or contaminants can be equipped with protective measures. Seals, gaskets, or covers can be employed to prevent the ingress of particles into the spline engagement. These protective measures help maintain the integrity of the spline profile, minimize wear, and ensure smooth operation even in dirty or dusty conditions.
4. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication is essential for the reliable operation of spline shafts, especially in challenging environmental conditions. Lubricants with appropriate viscosity and additives can be selected to provide effective lubrication and protection against wear, friction, and corrosion. Regular maintenance and lubrication intervals should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the spline shaft.
5. Shock and Vibration Resistance:
Spline shafts are designed to withstand shock and vibration encountered in various applications. The spline engagement and shaft design can incorporate features such as tighter tolerances, increased contact area, or damping elements to minimize the effects of shock and vibration. Additionally, proper fastening and mounting techniques help secure the shaft and reduce the risk of loosening or failure due to dynamic loads.
6. Environmental Sealing:
In certain applications where spline shafts are exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as underwater or in chemical environments, environmental sealing can be employed. Sealing methods such as O-rings, gaskets, or specialized seals provide an additional barrier against external elements, ensuring the integrity and performance of the spline shaft.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Spline shafts used in specific industries or applications may need to comply with industry standards or regulations regarding environmental conditions. Manufacturers can design and test their spline shafts to meet these requirements, ensuring that the shafts can handle the specified environmental conditions and perform reliably.
By incorporating design considerations, appropriate materials, protective coatings, lubrication, and maintenance practices, spline shafts can effectively handle variations in environmental conditions. This enables them to maintain their functionality, performance, and longevity even in challenging operating environments.
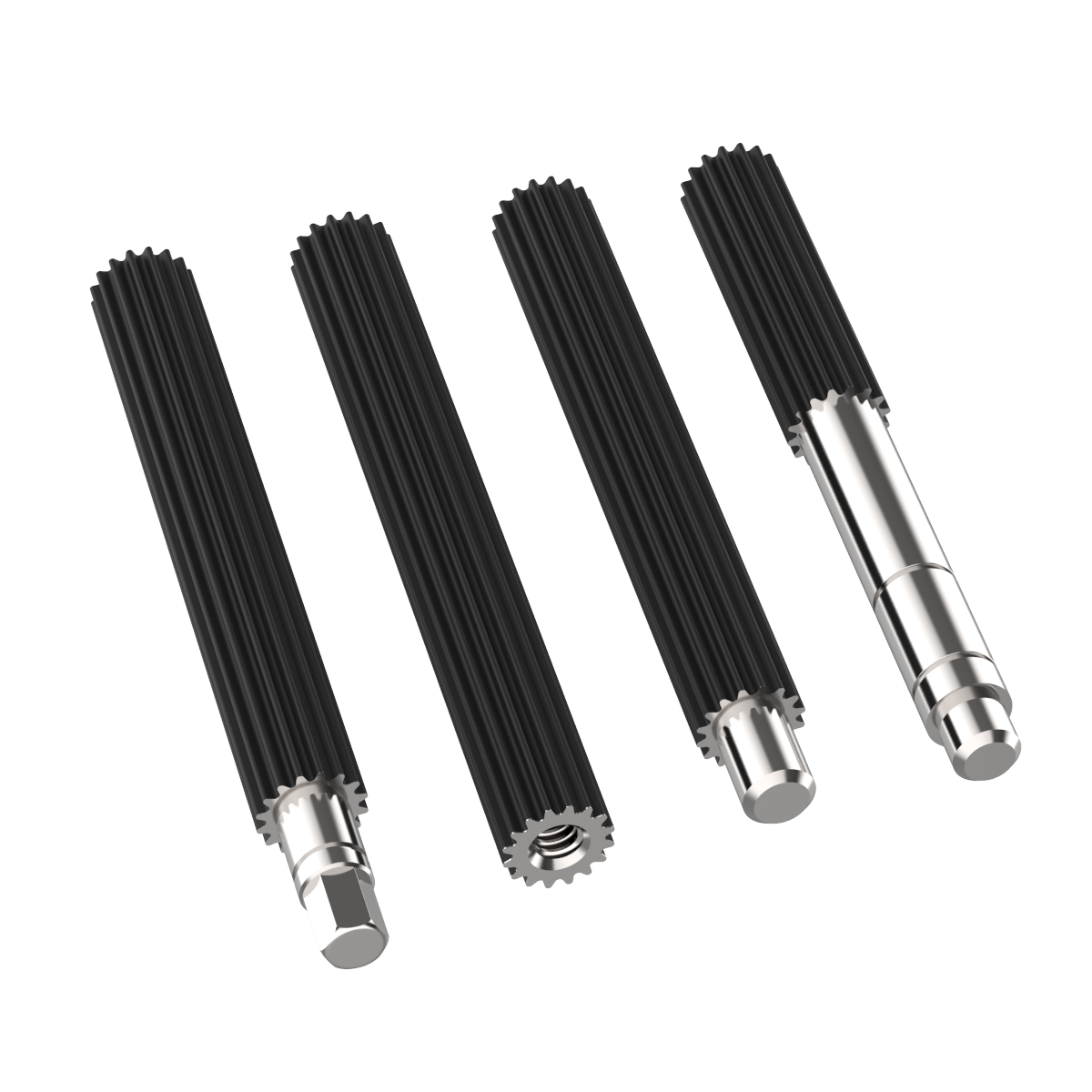
What are the key components and design features of a spline shaft?
A spline shaft consists of several key components and incorporates specific design features to ensure its functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Shaft Body:
The main component of a spline shaft is the shaft body, which provides the structural integrity and serves as the base for the spline features. The shaft body is typically cylindrical in shape and made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, or other alloyed metals. The material selection depends on factors like the application requirements, torque loads, and environmental conditions.
2. Splines:
The splines are the key design feature of a spline shaft. They are ridges or teeth that are machined onto the surface of the shaft. The splines create the interlocking mechanism with mating components, allowing for torque transmission and relative movement. The number, size, and shape of the splines can vary depending on the application requirements and design specifications.
3. Spline Profile:
The spline profile refers to the specific shape or geometry of the splines. Common types of spline profiles include involute, straight-sided, and serrated. The spline profile is chosen based on factors such as the torque transmission requirements, load distribution, and the desired engagement characteristics with mating components. The spline profile ensures optimal contact and torque transfer between the spline shaft and the mating component.
4. Spline Fit:
The spline fit refers to the dimensional relationship between the spline shaft and the mating component. It determines the clearance or interference between the splines, ensuring proper engagement and transmission of torque. The spline fit can be categorized into different classes, such as clearance fit, transition fit, or interference fit, based on the desired level of clearance or interference.
5. Surface Finish:
The surface finish of the spline shaft is crucial for its performance. The splines and the shaft body should have a smooth and consistent surface finish to minimize friction, wear, and the risk of stress concentrations. The surface finish can be achieved through machining, grinding, or other surface treatment methods to meet the required specifications.
6. Lubrication:
To ensure smooth operation and reduce wear, lubrication is often employed for spline shafts. Lubricants with appropriate viscosity and lubricating properties are applied to the spline interface to minimize friction, dissipate heat, and prevent premature wear or damage to the splines and mating components. Lubrication also helps in maintaining the functionality and prolonging the service life of the spline shaft.
7. Machining Tolerances:
Precision machining is critical for spline shafts to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and ensure proper engagement with mating components. Tight machining tolerances are maintained during the manufacturing process to ensure the spline profile, dimensions, and surface finish meet the specified design requirements. This ensures the interchangeability and compatibility of spline shafts in various applications.
In summary, the key components and design features of a spline shaft include the shaft body, splines, spline profile, spline fit, surface finish, lubrication, and machining tolerances. These elements work together to enable torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution while ensuring the functionality, durability, and performance of the spline shaft.


editor by CX 2024-03-08
China Best Sales Auto Spare Parts Spline Shaft OEM: Bg1t4234A Used for CZPT Ranger 1998/2005 Truck Automobile Rear Axle Drive Shaft
Product Description
Product Description
PACKUP TRUCKS.Drive Shaft
Drive shaft product model : ND05003
| Product name | rear axle drive shaft |
| OEM number | FORD: BG1T4234A |
| Material | 40cr carbon steel |
| Hole | 5 |
| Length | 684(mm) |
| Spline shaft | z=30 |
| Quality | High performance |
| Function of drive shaft | Power transmission |
| Vehicle model of drive shaft | FORD RANGER 1998/2005 |
| Processing of shaft | Forging |
| Surface treatment of shaft | Usually black customizable Silver, Blue, Rose Gold |
| Availability | Can be customized according to drawings |
We also sell chassis accessories for automobiles, trucks, agricultural machinery and construction machinery, including:
CVJ,Drive shaft, steering drive shaft, differential parts and assemblies, ball joints, universal joints, tire screws, and so on
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: Which payment terms will you accept?
A: We can accept TT, Western union, paypal and cash etc
Q: When my order will be shipped?
A:Once we get payment, we will ship your order within 20 working days.
Q: Which shipping will you offer?
A:By sea, air, DHL, Fedex, TNT, UPS, EMS, SF
Q: How long does it take to my address?
A:The normal delivery time is 20days, depending on which country you are in.
Q: How can I trace my order?
A:We will send you the tracking number by email.
Q: If I am not satisfied with the products, what should I do?
A:You can contact us and tell us about your problem. We will offer exchange or repair service under warranty.
| Material: | 40cr Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can spline shafts be used in both mobile and stationary machinery?
Yes, spline shafts can be used in both mobile and stationary machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Mobile Machinery:
Spline shafts find extensive use in various types of mobile machinery. For example:
- In Automotive Applications: Spline shafts are commonly used in automotive drivetrains, where they transmit torque from the engine to the wheels. They are found in components such as the transmission, differential, and axle shafts.
- In Construction and Earthmoving Equipment: Spline shafts are utilized in construction machinery, such as excavators, loaders, and bulldozers. They are employed in the powertrain systems to transfer torque and drive the hydraulic pumps or propel the machine.
- In Agricultural Equipment: Spline shafts are used in agricultural machinery like tractors, combines, and harvesters. They help transfer power from the engine to various driven components, such as the wheels, PTO (power take-off), or hydraulic systems.
- In Off-Road Vehicles: Spline shafts are present in off-road vehicles, including ATVs (all-terrain vehicles) and military vehicles. They enable power transmission to the wheels or drivetrain components, ensuring mobility and performance in challenging terrains.
2. Stationary Machinery:
Spline shafts are also widely employed in stationary machinery across various industries. Some examples include:
- In Machine Tools: Spline shafts are used in machine tools, such as lathes, milling machines, and grinding machines. They provide torque transmission in the spindle or lead screw mechanisms, enabling precision motion control and material removal operations.
- In Industrial Gearboxes: Spline shafts play a crucial role in industrial gearboxes used in manufacturing and processing plants. They transmit torque between input and output shafts, enabling speed reduction or increase as required by the application.
- In Power Generation: Spline shafts are utilized in power generation equipment, including turbines and generators. They help transmit torque between the rotating rotor and the stationary components, facilitating energy conversion.
- In Pump and Compressor Systems: Spline shafts are present in pumps and compressors used in various industries. They transmit torque from the motor or prime mover to the impeller or compressor elements, enabling fluid or gas transfer.
The versatility of spline shafts makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, both mobile and stationary. Their ability to efficiently transmit torque, accommodate misalignment, distribute loads, and provide reliable connections makes them a preferred choice in diverse machinery across industries.

How do spline shafts handle variations in load capacity and weight?
Spline shafts are designed to handle variations in load capacity and weight in mechanical systems. Here’s how they accomplish this:
1. Material Selection:
Spline shafts are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel or alloy, chosen for their ability to withstand heavy loads and provide durability. The selection of materials takes into account factors such as tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance to ensure the shaft can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
2. Engineering Design:
Spline shafts are designed with consideration for the anticipated loads and weights they will encounter. The dimensions, profile, and number of splines are determined based on the expected torque requirements and the magnitude of the applied loads. By carefully engineering the design, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight while maintaining structural integrity and reliable performance.
3. Load Distribution:
The interlocking engagement of spline shafts allows for effective load distribution along the length of the shaft. This helps distribute the applied loads evenly, preventing localized stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of deformation or failure. By distributing the load, spline shafts can handle variations in load capacity and weight without compromising their performance.
4. Structural Reinforcement:
In applications with higher load capacities or heavier weights, spline shafts may incorporate additional structural features to enhance their strength. This can include thicker spline teeth, larger spline diameters, or reinforced sections along the shaft. By reinforcing critical areas, spline shafts can handle increased loads and weights while maintaining their integrity.
5. Lubrication and Surface Treatment:
Proper lubrication is essential for spline shafts to handle variations in load capacity and weight. Lubricants reduce friction between the mating surfaces, minimizing wear and preventing premature failure. Additionally, surface treatments such as coatings or heat treatments can enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the spline shaft, improving its ability to handle varying loads and weights.
6. Testing and Validation:
Spline shafts undergo rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet the specified load capacity and weight requirements. This may involve laboratory testing, simulation analysis, or field testing under real-world conditions. By subjecting spline shafts to thorough testing, manufacturers can verify their performance and ensure they can handle variations in load capacity and weight.
Overall, spline shafts are designed and engineered to handle variations in load capacity and weight by utilizing appropriate materials, optimizing the design, distributing loads effectively, incorporating structural reinforcement when necessary, implementing proper lubrication and surface treatments, and conducting thorough testing and validation. These measures enable spline shafts to reliably transmit torque and handle varying loads in diverse mechanical applications.

What is a spline shaft and what is its primary function?
A spline shaft is a mechanical component that consists of a series of ridges or teeth (called splines) that are machined onto the surface of the shaft. Its primary function is to transmit torque while allowing for the relative movement or sliding of mating components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Structure and Design:
A spline shaft typically has a cylindrical shape with external or internal splines. The external spline shaft has splines on the outer surface, while the internal spline shaft has splines on the inner bore. The number, size, and shape of the splines can vary depending on the specific application and design requirements.
2. Torque Transmission:
The main function of a spline shaft is to transmit torque between two mating components, such as gears, couplings, or other rotational elements. The splines on the shaft engage with corresponding splines on the mating component, creating a mechanical interlock. When torque is applied to the spline shaft, the engagement between the splines ensures that the rotational force is transferred from the shaft to the mating component, allowing the system to transmit power.
3. Relative Movement:
Unlike other types of shafts, a spline shaft allows for relative movement or sliding between the shaft and the mating component. This sliding motion can be axial (along the shaft’s axis) or radial (perpendicular to the shaft’s axis). The splines provide a precise and controlled interface that allows for this movement while maintaining torque transmission. This feature is particularly useful in applications where axial or radial displacement or misalignment needs to be accommodated.
4. Load Distribution:
Another important function of a spline shaft is to distribute the applied load evenly along its length. The splines create multiple contact points between the shaft and the mating component, which helps to distribute the torque and axial or radial forces over a larger surface area. This load distribution minimizes stress concentrations and reduces the risk of premature wear or failure.
5. Versatility and Applications:
Spline shafts find applications in various industries and systems, including automotive, aerospace, machinery, and power transmission. They are commonly used in gearboxes, drive systems, power take-off units, steering systems, and many other rotational mechanisms where torque transmission, relative movement, and load distribution are essential.
6. Design Considerations:
When designing a spline shaft, factors such as the torque requirements, speed, applied loads, and environmental conditions need to be considered. The spline geometry, material selection, and surface finish are critical for ensuring proper engagement, load-bearing capacity, and durability of the spline shaft.
In summary, a spline shaft is a mechanical component with splines that allows for torque transmission while accommodating relative movement or sliding between mating components. Its primary function is to transmit rotational force, distribute loads, and enable axial or radial displacement in various applications requiring precise torque transfer and flexibility.


editor by CX 2023-10-24
China Custom Truck Spare Parts Spline Shaft OEM: 42311-2760 Used for Hino Ranger Dump Truck Superior Quality Rear Axle Drive Shaft carbon fiber drive shaft
Product Description
Product Description
rear axle half axle OEM:42311-2760 for HINO rear wheel half axle shaft
| Modle | Oem | Number of gear | The length of the(mm) | Hole count |
| HINO | 42311-2480 | 34 | 1045 | 8+2 |
| HINO | 42311-3260 | 29 | 1104 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2760 | 29 | 1039 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3330 | 31 | 1030 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3480 | 31 | 1109 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3470 | 31 | 965 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2200 | 29 | 1067 | 10+2 |
| HINO | 42311-1460 | 29 | 991 | 10+2 |
| HINO | 42311-1430 | 29 | 1016 | 10+2 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 970 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 990 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1571 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1030 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1050 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1070 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1090 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1110 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3890 | 34 | 1130 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3260 RANGER | 29 | 1104/43.46 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2760 RANGER | 29 | 1039/40.90 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3330 JUMO | 31 | 1030/40.55 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3480 JUMO | 31 | 1109/43.66 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3470 JUMO | 31 | 965/37.99 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2200 KT42 | 29 | 1067/42.0 | 10+2 |
| HINO | 42311-1460 KT39 | 29 | 991/39.0 | 10+2 |
| HINO | 42311-1430 KT40 | 29 | 1016/40.0 | 10+2 |
| HINO | 42311-3690 | 34 | 970/38.18 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3720 | 34 | 1000/39.37 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2590 | 34 | 1571/40.16 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2530 | 34 | 1030/40.55 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2460 | 34 | 1050/41.34 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3711 | 34 | 1070/42.16 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3710 | 34 | 1090/42.90 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-2450 | 34 | 1110/43.70 | 10 |
| HINO | 42311-3700 | 34 | 1130/44.50 | 10 |
| HINO | 34 | 1095/43.1 | 8+2 |
Company Profile
FAQ
Q:Can you do OEM and provide samples firstly?
A:Yes,OEM and ODM are welcomed ,and with stocks ,samples can be shipped with 3 HangZhou as you need.
Q:What is the MOQ?payment term? and delivery time
A:For regular products, MOQ: 100PCS each model;
Once we get payment, we will ship your order within 20 working days.
The normal delivery time is 20days, depending on which country you are in.
Q:Where are you? Can we visit your factory?
A:Our factory is located in HangZhou, ZheJiang , China.
lt is close to HangZhou Airport, and the traffic at the west exit of HangZhou Sanquan Expressway is very convenient.
All employees of the company sincerely welcome domestic and foreign merchants to visit our company for guidance and business negotiation.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated|
|
|---|
| After-sales Service: | 1year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 1 |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

The Benefits of Spline Couplings for Disc Brake Mounting Interfaces
Spline couplings are commonly used for securing disc brake mounting interfaces. Spline couplings are often used in high-performance vehicles, aeronautics, and many other applications. However, the mechanical benefits of splines are not immediately obvious. Listed below are the benefits of spline couplings. We’ll discuss what these advantages mean for you. Read on to discover how these couplings work.
Disc brake mounting interfaces are splined
There are two common disc brake mounting interfaces – splined and six-bolt. Splined rotors fit on splined hubs; six-bolt rotors will need an adapter to fit on six-bolt hubs. The six-bolt method is easier to maintain and may be preferred by many cyclists. If you’re thinking of installing a disc brake system, it is important to know how to choose the right splined and center lock interfaces.
Aerospace applications
The splines used for spline coupling in aircraft are highly complex. While some previous researches have addressed the design of splines, few publications have tackled the problem of misaligned spline coupling. Nevertheless, the accurate results we obtained were obtained using dedicated simulation tools, which are not commercially available. Nevertheless, such tools can provide a useful reference for our approach. It would be beneficial if designers could use simple tools for evaluating contact pressure peaks. Our analytical approach makes it possible to find answers to such questions.
The design of a spline coupling for aerospace applications must be accurate to minimize weight and prevent failure mechanisms. In addition to weight reduction, it is necessary to minimize fretting fatigue. The pressure distribution on the spline coupling teeth is a significant factor in determining its fretting fatigue. Therefore, we use analytical and experimental methods to examine the contact pressure distribution in the axial direction of spline couplings.
The teeth of a spline coupling can be categorized by the type of engagement they provide. This study investigates the position of resultant contact forces in the teeth of a spline coupling when applied to pitch diameter. Using FEM models, numerical results are generated for nominal and parallel offset misalignments. The axial tooth profile determines the behavior of the coupling component and its ability to resist wear. Angular misalignment is also a concern, causing misalignment.
In order to assess wear damage of a spline coupling, we must take into consideration the impact of fretting on the components. This wear is caused by relative motion between the teeth that engage them. The misalignment may be caused by vibrations, cyclical tooth deflection, or angular misalignment. The result of this analysis may help designers improve their spline coupling designs and develop improved performance.
CZPT polyimide, an abrasion-resistant polymer, is a popular choice for high-temperature spline couplings. This material reduces friction and wear, provides a low friction surface, and has a low wear rate. Furthermore, it offers up to 50 times the life of metal on metal spline connections. For these reasons, it is important to choose the right material for your spline coupling.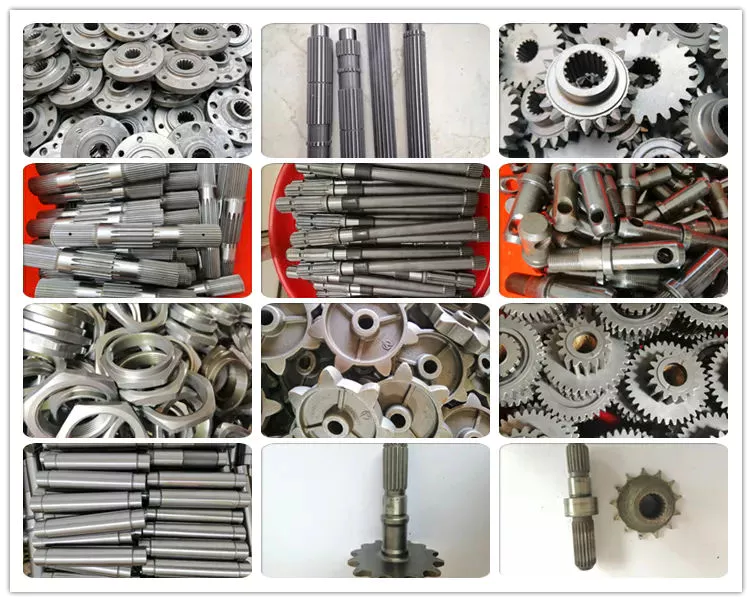
High-performance vehicles
A spline coupler is a device used to connect splined shafts. A typical spline coupler resembles a short pipe with splines on either end. There are two basic types of spline coupling: single and dual spline. One type attaches to a drive shaft, while the other attaches to the gearbox. While spline couplings are typically used in racing, they’re also used for performance problems.
The key challenge in spline couplings is to determine the optimal dimension of spline joints. This is difficult because no commercial codes allow the simulation of misaligned joints, which can destroy components. This article presents analytical approaches to estimating contact pressures in spline connections. The results are comparable with numerical approaches but require special codes to accurately model the coupling operation. This research highlights several important issues and aims to make the application of spline couplings in high-performance vehicles easier.
The stiffness of spline assemblies can be calculated using tooth-like structures. Such splines can be incorporated into the spline joint to produce global stiffness for torsional vibration analysis. Bearing reactions are calculated for a certain level of misalignment. This information can be used to design bearing dimensions and correct misalignment. There are three types of spline couplings.
Major diameter fit splines are made with tightly controlled outside diameters. This close fit provides concentricity transfer from the male to the female spline. The teeth of the male spline usually have chamfered tips and clearance with fillet radii. These splines are often manufactured from billet steel or aluminum. These materials are renowned for their strength and uniform grain created by the forging process. ANSI and DIN design manuals define classes of fit.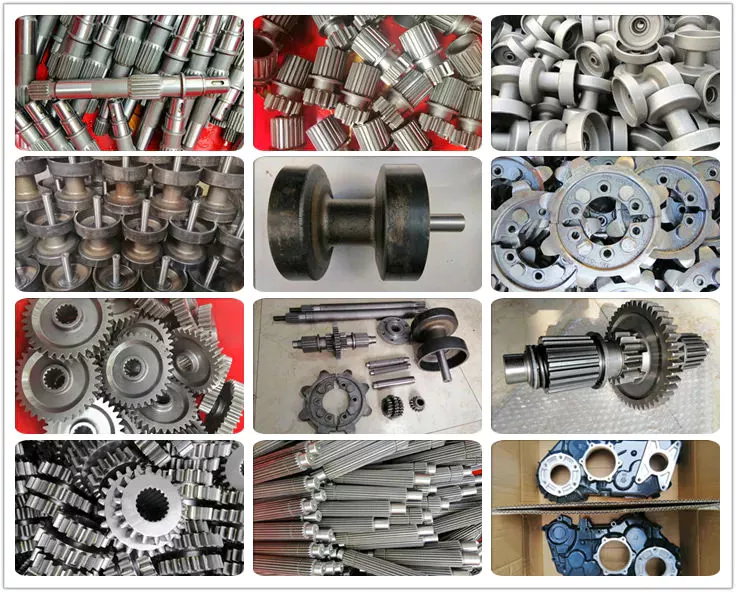
Disc brake mounting interfaces
A spline coupling for disc brake mounting interfaces is a type of hub-to-brake-disc mount. It is a highly durable coupling mechanism that reduces heat transfer from the disc to the axle hub. The mounting arrangement also isolates the axle hub from direct contact with the disc. It is also designed to minimize the amount of vehicle downtime and maintenance required to maintain proper alignment.
Disc brakes typically have substantial metal-to-metal contact with axle hub splines. The discs are held in place on the hub by intermediate inserts. This metal-to-metal contact also aids in the transfer of brake heat from the brake disc to the axle hub. Spline coupling for disc brake mounting interfaces comprises a mounting ring that is either a threaded or non-threaded spline.
During drag brake experiments, perforated friction blocks filled with various additive materials are introduced. The materials included include Cu-based powder metallurgy material, a composite material, and a Mn-Cu damping alloy. The filling material affects the braking interface’s wear behavior and friction-induced vibration characteristics. Different filling materials produce different types of wear debris and have different wear evolutions. They also differ in their surface morphology.
Disc brake couplings are usually made of two different types. The plain and HD versions are interchangeable. The plain version is the simplest to install, while the HD version has multiple components. The two-piece couplings are often installed at the same time, but with different mounting interfaces. You should make sure to purchase the appropriate coupling for your vehicle. These interfaces are a vital component of your vehicle and must be installed correctly for proper operation.
Disc brakes use disc-to-hub elements that help locate the forces and displace them to the rim. These elements are typically made of stainless steel, which increases the cost of manufacturing the disc brake mounting interface. Despite their benefits, however, the high braking force loads they endure are hard on the materials. Moreover, excessive heat transferred to the intermediate elements can adversely affect the fatigue life and long-term strength of the brake system.


editor by CX 2023-06-05
China OEM Auto Spare Parts Spline Shaft OEM: 503355184 Used for CZPT Daily 1997/2015 Van Truck Automobile Rear Axle Drive Shaft differential drive shaft
Product Description
Product Description
SUV.PACKUP TRUCKS.Drive Shaft
Drive shaft product model : ND05001
| Product name | rear axle drive shaft |
| OEM number | 55715184 |
| Material | 40cr carbon steel |
| Hole | 8 |
| Length | 939(mm) |
| Spline shaft | z=32 |
| Quality | High performance |
| Function of drive shaft | Power transmission |
| Vehicle model of drive shaft | IVECO DAILY 1997/2015 |
| Processing of shaft | Forging |
| Surface treatment of shaft | Usually black customizable Silver, Blue, Rose Gold |
| Availability | Can be customized according to drawings |
We also sell chassis accessories for automobiles, trucks, agricultural machinery and construction machinery, including:
CVJ,Drive shaft, steering drive shaft, differential parts and assemblies, ball joints, universal joints, tire screws, and so on
Company Profile
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated|
|
|---|
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

The Benefits of Spline Couplings for Disc Brake Mounting Interfaces
Spline couplings are commonly used for securing disc brake mounting interfaces. Spline couplings are often used in high-performance vehicles, aeronautics, and many other applications. However, the mechanical benefits of splines are not immediately obvious. Listed below are the benefits of spline couplings. We’ll discuss what these advantages mean for you. Read on to discover how these couplings work.
Disc brake mounting interfaces are splined
There are two common disc brake mounting interfaces – splined and six-bolt. Splined rotors fit on splined hubs; six-bolt rotors will need an adapter to fit on six-bolt hubs. The six-bolt method is easier to maintain and may be preferred by many cyclists. If you’re thinking of installing a disc brake system, it is important to know how to choose the right splined and center lock interfaces.
Aerospace applications
The splines used for spline coupling in aircraft are highly complex. While some previous researches have addressed the design of splines, few publications have tackled the problem of misaligned spline coupling. Nevertheless, the accurate results we obtained were obtained using dedicated simulation tools, which are not commercially available. Nevertheless, such tools can provide a useful reference for our approach. It would be beneficial if designers could use simple tools for evaluating contact pressure peaks. Our analytical approach makes it possible to find answers to such questions.
The design of a spline coupling for aerospace applications must be accurate to minimize weight and prevent failure mechanisms. In addition to weight reduction, it is necessary to minimize fretting fatigue. The pressure distribution on the spline coupling teeth is a significant factor in determining its fretting fatigue. Therefore, we use analytical and experimental methods to examine the contact pressure distribution in the axial direction of spline couplings.
The teeth of a spline coupling can be categorized by the type of engagement they provide. This study investigates the position of resultant contact forces in the teeth of a spline coupling when applied to pitch diameter. Using FEM models, numerical results are generated for nominal and parallel offset misalignments. The axial tooth profile determines the behavior of the coupling component and its ability to resist wear. Angular misalignment is also a concern, causing misalignment.
In order to assess wear damage of a spline coupling, we must take into consideration the impact of fretting on the components. This wear is caused by relative motion between the teeth that engage them. The misalignment may be caused by vibrations, cyclical tooth deflection, or angular misalignment. The result of this analysis may help designers improve their spline coupling designs and develop improved performance.
CZPT polyimide, an abrasion-resistant polymer, is a popular choice for high-temperature spline couplings. This material reduces friction and wear, provides a low friction surface, and has a low wear rate. Furthermore, it offers up to 50 times the life of metal on metal spline connections. For these reasons, it is important to choose the right material for your spline coupling.
High-performance vehicles
A spline coupler is a device used to connect splined shafts. A typical spline coupler resembles a short pipe with splines on either end. There are two basic types of spline coupling: single and dual spline. One type attaches to a drive shaft, while the other attaches to the gearbox. While spline couplings are typically used in racing, they’re also used for performance problems.
The key challenge in spline couplings is to determine the optimal dimension of spline joints. This is difficult because no commercial codes allow the simulation of misaligned joints, which can destroy components. This article presents analytical approaches to estimating contact pressures in spline connections. The results are comparable with numerical approaches but require special codes to accurately model the coupling operation. This research highlights several important issues and aims to make the application of spline couplings in high-performance vehicles easier.
The stiffness of spline assemblies can be calculated using tooth-like structures. Such splines can be incorporated into the spline joint to produce global stiffness for torsional vibration analysis. Bearing reactions are calculated for a certain level of misalignment. This information can be used to design bearing dimensions and correct misalignment. There are three types of spline couplings.
Major diameter fit splines are made with tightly controlled outside diameters. This close fit provides concentricity transfer from the male to the female spline. The teeth of the male spline usually have chamfered tips and clearance with fillet radii. These splines are often manufactured from billet steel or aluminum. These materials are renowned for their strength and uniform grain created by the forging process. ANSI and DIN design manuals define classes of fit.
Disc brake mounting interfaces
A spline coupling for disc brake mounting interfaces is a type of hub-to-brake-disc mount. It is a highly durable coupling mechanism that reduces heat transfer from the disc to the axle hub. The mounting arrangement also isolates the axle hub from direct contact with the disc. It is also designed to minimize the amount of vehicle downtime and maintenance required to maintain proper alignment.
Disc brakes typically have substantial metal-to-metal contact with axle hub splines. The discs are held in place on the hub by intermediate inserts. This metal-to-metal contact also aids in the transfer of brake heat from the brake disc to the axle hub. Spline coupling for disc brake mounting interfaces comprises a mounting ring that is either a threaded or non-threaded spline.
During drag brake experiments, perforated friction blocks filled with various additive materials are introduced. The materials included include Cu-based powder metallurgy material, a composite material, and a Mn-Cu damping alloy. The filling material affects the braking interface’s wear behavior and friction-induced vibration characteristics. Different filling materials produce different types of wear debris and have different wear evolutions. They also differ in their surface morphology.
Disc brake couplings are usually made of two different types. The plain and HD versions are interchangeable. The plain version is the simplest to install, while the HD version has multiple components. The two-piece couplings are often installed at the same time, but with different mounting interfaces. You should make sure to purchase the appropriate coupling for your vehicle. These interfaces are a vital component of your vehicle and must be installed correctly for proper operation.
Disc brakes use disc-to-hub elements that help locate the forces and displace them to the rim. These elements are typically made of stainless steel, which increases the cost of manufacturing the disc brake mounting interface. Despite their benefits, however, the high braking force loads they endure are hard on the materials. Moreover, excessive heat transferred to the intermediate elements can adversely affect the fatigue life and long-term strength of the brake system.


editor by CX 2023-05-12
China supplier Auto Spare Parts Spline Shaft OEM: 7890903067087 Used for CZPT F-4000 2004/2016 Truck Automobile Rear Axle Agriculture Drive Shaft drive shaft electric motor
Product Description
Product Description
TRUCK.Drive Shaft
Drive shaft product model : ND05002
| Product name | rear axle drive shaft |
| OEM number | 87 |
| Material | 40cr carbon steel |
| Hole | 8 |
| Length | 950(mm) |
| Spline shaft | z=37 |
| Quality | High performance |
| Function of drive shaft | Power transmission |
| Vehicle model of drive shaft | FORD F-4000 2004/2016 |
| Processing of shaft | Forging |
| Surface treatment of shaft | Usually black customizable Silver, Blue, Rose Gold |
| Availability | Can be customized according to drawings |
We also sell chassis accessories for automobiles, trucks, agricultural machinery and construction machinery, including:
CVJ,Drive shaft, steering drive shaft, differential parts and assemblies, ball joints, universal joints, tire screws, and so on
Company Profile
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated|
|
|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
|---|---|
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Types of Splines
There are four types of splines: Involute, Parallel key, helical, and ball. Learn about their characteristics. And, if you’re not sure what they are, you can always request a quotation. These splines are commonly used for building special machinery, repair jobs, and other applications. The CZPT Manufacturing Company manufactures these shafts. It is a specialty manufacturer and we welcome your business.
Involute splines
The involute spline provides a more rigid and durable structure, and is available in a variety of diameters and spline counts. Generally, steel, carbon steel, or titanium are used as raw materials. Other materials, such as carbon fiber, may be suitable. However, titanium can be difficult to produce, so some manufacturers make splines using other constituents.
When splines are used in shafts, they prevent parts from separating during operation. These features make them an ideal choice for securing mechanical assemblies. Splines with inward-curving grooves do not have sharp corners and are therefore less likely to break or separate while they are in operation. These properties help them to withstand high-speed operations, such as braking, accelerating, and reversing.
A male spline is fitted with an externally-oriented face, and a female spline is inserted through the center. The teeth of the male spline typically have chamfered tips to provide clearance with the transition area. The radii and width of the teeth of a male spline are typically larger than those of a female spline. These specifications are specified in ANSI or DIN design manuals.
The effective tooth thickness of a spline depends on the involute profile error and the lead error. Also, the spacing of the spline teeth and keyways can affect the effective tooth thickness. Involute splines in a splined shaft are designed so that at least 25 percent of the spline teeth engage during coupling, which results in a uniform distribution of load and wear on the spline.
Parallel key splines
A parallel splined shaft has a helix of equal-sized grooves around its circumference. These grooves are generally parallel or involute. Splines minimize stress concentrations in stationary joints and allow linear and rotary motion. Splines may be cut or cold-rolled. Cold-rolled splines have more strength than cut spines and are often used in applications that require high strength, accuracy, and a smooth surface.
A parallel key splined shaft features grooves and keys that are parallel to the axis of the shaft. This design is best suited for applications where load bearing is a primary concern and a smooth motion is needed. A parallel key splined shaft can be made from alloy steels, which are iron-based alloys that may also contain chromium, nickel, molybdenum, copper, or other alloying materials.
A splined shaft can be used to transmit torque and provide anti-rotation when operating as a linear guide. These shafts have square profiles that match up with grooves in a mating piece and transmit torque and rotation. They can also be easily changed in length, and are commonly used in aerospace. Its reliability and fatigue life make it an excellent choice for many applications.
The main difference between a parallel key splined shaft and a keyed shaft is that the former offers more flexibility. They lack slots, which reduce torque-transmitting capacity. Splines offer equal load distribution along the gear teeth, which translates into a longer fatigue life for the shaft. In agricultural applications, shaft life is essential. Agricultural equipment, for example, requires the ability to function at high speeds for extended periods of time.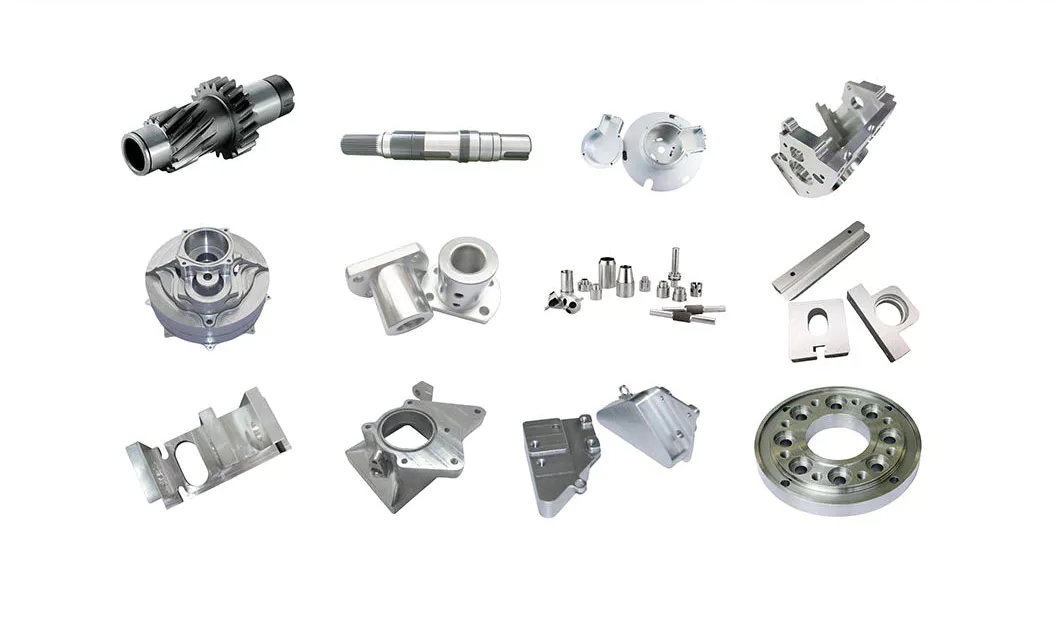
Involute helical splines
Involute splines are a common design for splined shafts. They are the most commonly used type of splined shaft and feature equal spacing among their teeth. The teeth of this design are also shorter than those of the parallel spline shaft, reducing stress concentration. These splines can be used to transmit power to floating or permanently fixed gears, and reduce stress concentrations in the stationary joint. Involute splines are the most common type of splined shaft, and are widely used for a variety of applications in automotive, machine tools, and more.
Involute helical spline shafts are ideal for applications involving axial motion and rotation. They allow for face coupling engagement and disengagement. This design also allows for a larger diameter than a parallel spline shaft. The result is a highly efficient gearbox. Besides being durable, splines can also be used for other applications involving torque and energy transfer.
A new statistical model can be used to determine the number of teeth that engage for a given load. These splines are characterized by a tight fit at the major diameters, thereby transferring concentricity from the shaft to the female spline. A male spline has chamfered tips for clearance with the transition area. ANSI and DIN design manuals specify the different classes of fit.
The design of involute helical splines is similar to that of gears, and their ridges or teeth are matched with the corresponding grooves in a mating piece. It enables torque and rotation to be transferred to a mate piece while maintaining alignment of the two components. Different types of splines are used in different applications. Different splines can have different levels of tooth height.
Involute ball splines
When splines are used, they allow the shaft and hub to engage evenly over the shaft’s entire circumference. Because the teeth are evenly spaced, the load that they can transfer is uniform and their position is always the same regardless of shaft length. Whether the shaft is used to transmit torque or to transmit power, splines are a great choice. They provide maximum strength and allow for linear or rotary motion.
There are three basic types of splines: helical, crown, and ball. Crown splines feature equally spaced grooves. Crown splines feature involute sides and parallel sides. Helical splines use involute teeth and are often used in small diameter shafts. Ball splines contain a ball bearing inside the splined shaft to facilitate rotary motion and minimize stress concentration in stationary joints.
The two types of splines are classified under the ANSI classes of fit. Fillet root splines have teeth that mesh along the longitudinal axis of rotation. Flat root splines have similar teeth, but are intended to optimize strength for short-term use. Both types of splines are important for ensuring the shaft aligns properly and is not misaligned.
The friction coefficient of the hub is a complex process. When the hub is off-center, the center moves in predictable but irregular motion. Moreover, when the shaft is centered, the center may oscillate between being centered and being off-center. To compensate for this, the torque must be adequate to keep the shaft in its axis during all rotation angles. While straight-sided splines provide similar centering, they have lower misalignment load factors.
Keyed shafts
Essentially, splined shafts have teeth or ridges that fit together to transfer torque. Because splines are not as tall as involute gears, they offer uniform torque transfer. Additionally, they provide the opportunity for torque and rotational changes and improve wear resistance. In addition to their durability, splined shafts are popular in the aerospace industry and provide increased reliability and fatigue life.
Keyed shafts are available in different materials, lengths, and diameters. When used in high-power drive applications, they offer higher torque and rotational speeds. The higher torque they produce helps them deliver power to the gearbox. However, they are not as durable as splined shafts, which is why the latter is usually preferred in these applications. And while they’re more expensive, they’re equally effective when it comes to torque delivery.
Parallel keyed shafts have separate profiles and ridges and are used in applications requiring accuracy and precision. Keyed shafts with rolled splines are 35% stronger than cut splines and are used where precision is essential. These splines also have a smooth finish, which can make them a good choice for precision applications. They also work well with gears and other mechanical systems that require accurate torque transfer.
Carbon steel is another material used for splined shafts. Carbon steel is known for its malleability, and its shallow carbon content helps create reliable motion. However, if you’re looking for something more durable, consider ferrous steel. This type contains metals such as nickel, chromium, and molybdenum. And it’s important to remember that carbon steel is not the only material to consider.


editor by CX 2023-04-26
China rotary tiller spare parts joint shaft pto for agricultural machine tractor parts a line drive shaft
Problem: New
Warranty: 6 Months
Applicable Industries: Equipment Fix Outlets, Farms
Weight (KG): twenty five KG
Showroom Spot: None
Video clip outgoing-inspection: Provided
Equipment Check Report: Offered
Advertising and marketing Kind: New Product 2571
Sort: Shafts
Use: Tractors
Color:: Yellow or Black
tube:: Triangle /Lemon /Star /Involute Spline Tube
Yoke:: same as tube
Certification: ce
Merchandise Name:: Agricultural PTO Travel Shaft
Application: Cultivators
Deal: individuals
Dimensions: numerous measurements
Model: cxnofia
Utilised for: Tractors
Packaging Specifics: Neutral Cartons and Pallets for free fumigation if there is no unique requirments. It is accessible to offer vibrant package according to your design
Port: shangha
Our Solutions
A. EXW,FOB,CIF AND OTHER Typical International TRADE RULE ARE Acknowledged!B. D/P,L/C,T/T AND OTHER Regular Kind OF PAYMENT,IF THE Purchase Whole ACCOUNT Reduce THAN $1,000.00,WE CAN Settle for PAYMENT BY PAYPAL,WESTERN UNION, Wholesale Higher Top quality CGL 2 Wheel Bike Sprocket Wheel Hub Areas Wheel Seat Assembly MONEYGRAM AND OTHER Swift PAYMENT.C. ON LINE FOR 24HOURS Services.
D. ALL Goods FROM OUR Manufacturing unit WILL BE GURANTEED
Agricultural PTO Travel Shaft
1. You can pick the Tube, CrossJournal, Shield and Yoke in accordance to your needs.
Design Quantity/Cross Series: T01,T02,T03,T04,T05,T06,T07,T08 and some special cross Journal 2. Dimension/Dimensions: Minimal overall length: 600-1800mm or 27″-sixty” Team twenty hydraulic equipment pump KGP2A2-BB for tractor 3. Operating Issue: For Harvester, Vans and Agricultural Use 4. Defend Color: Yellow or black. 5. Material: Metal and Plastic 6. Tube: Triangular, Lemon, Star and Splined 7. Harvester side yoke: 6 or 21 splined drive pin yoke 8. Employ aspect yoke: 6 splined press pin shear bolt kind yoke
two.Broad Angle Joint, Shear Bolt Torque Limiter,Friction Torque Limiter3.Cross Journal Dimensions: Collection 1# to Series 8#
4.Splined Yokes: Press Pin, Ball Attachment,Collar Yoke4.Guarantee interval: 2 a long time
five.CE Certificate
Packaging & Gunaiyou TG-15CTAS-sixteen-five hundred and TG-20CTAS-sixteen-five hundred 11KW 15KW built-in screw air compressor Transport
Contact Us
How to Calculate Stiffness, Centering Force, Wear and Fatigue Failure of Spline Couplings
There are various types of spline couplings. These couplings have several important properties. These properties are: Stiffness, Involute splines, Misalignment, Wear and fatigue failure. To understand how these characteristics relate to spline couplings, read this article. It will give you the necessary knowledge to determine which type of coupling best suits your needs. Keeping in mind that spline couplings are usually spherical in shape, they are made of steel.
Involute splines
An effective side interference condition minimizes gear misalignment. When two splines are coupled with no spline misalignment, the maximum tensile root stress shifts to the left by five mm. A linear lead variation, which results from multiple connections along the length of the spline contact, increases the effective clearance or interference by a given percentage. This type of misalignment is undesirable for coupling high-speed equipment.
Involute splines are often used in gearboxes. These splines transmit high torque, and are better able to distribute load among multiple teeth throughout the coupling circumference. The involute profile and lead errors are related to the spacing between spline teeth and keyways. For coupling applications, industry practices use splines with 25 to fifty-percent of spline teeth engaged. This load distribution is more uniform than that of conventional single-key couplings.
To determine the optimal tooth engagement for an involved spline coupling, Xiangzhen Xue and colleagues used a computer model to simulate the stress applied to the splines. The results from this study showed that a “permissible” Ruiz parameter should be used in coupling. By predicting the amount of wear and tear on a crowned spline, the researchers could accurately predict how much damage the components will sustain during the coupling process.
There are several ways to determine the optimal pressure angle for an involute spline. Involute splines are commonly measured using a pressure angle of 30 degrees. Similar to gears, involute splines are typically tested through a measurement over pins. This involves inserting specific-sized wires between gear teeth and measuring the distance between them. This method can tell whether the gear has a proper tooth profile.
The spline system shown in Figure 1 illustrates a vibration model. This simulation allows the user to understand how involute splines are used in coupling. The vibration model shows four concentrated mass blocks that represent the prime mover, the internal spline, and the load. It is important to note that the meshing deformation function represents the forces acting on these three components.
Stiffness of coupling
The calculation of stiffness of a spline coupling involves the measurement of its tooth engagement. In the following, we analyze the stiffness of a spline coupling with various types of teeth using two different methods. Direct inversion and blockwise inversion both reduce CPU time for stiffness calculation. However, they require evaluation submatrices. Here, we discuss the differences between these two methods.
The analytical model for spline couplings is derived in the second section. In the third section, the calculation process is explained in detail. We then validate this model against the FE method. Finally, we discuss the influence of stiffness nonlinearity on the rotor dynamics. Finally, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method. We present a simple yet effective method for estimating the lateral stiffness of spline couplings.
The numerical calculation of the spline coupling is based on the semi-analytical spline load distribution model. This method involves refined contact grids and updating the compliance matrix at each iteration. Hence, it consumes significant computational time. Further, it is difficult to apply this method to the dynamic analysis of a rotor. This method has its own limitations and should be used only when the spline coupling is fully investigated.
The meshing force is the force generated by a misaligned spline coupling. It is related to the spline thickness and the transmitting torque of the rotor. The meshing force is also related to the dynamic vibration displacement. The result obtained from the meshing force analysis is given in Figures 7, 8, and 9.
The analysis presented in this paper aims to investigate the stiffness of spline couplings with a misaligned spline. Although the results of previous studies were accurate, some issues remained. For example, the misalignment of the spline may cause contact damages. The aim of this article is to investigate the problems associated with misaligned spline couplings and propose an analytical approach for estimating the contact pressure in a spline connection. We also compare our results to those obtained by pure numerical approaches.
Misalignment
To determine the centering force, the effective pressure angle must be known. Using the effective pressure angle, the centering force is calculated based on the maximum axial and radial loads and updated Dudley misalignment factors. The centering force is the maximum axial force that can be transmitted by friction. Several published misalignment factors are also included in the calculation. A new method is presented in this paper that considers the cam effect in the normal force.
In this new method, the stiffness along the spline joint can be integrated to obtain a global stiffness that is applicable to torsional vibration analysis. The stiffness of bearings can also be calculated at given levels of misalignment, allowing for accurate estimation of bearing dimensions. It is advisable to check the stiffness of bearings at all times to ensure that they are properly sized and aligned.
A misalignment in a spline coupling can result in wear or even failure. This is caused by an incorrectly aligned pitch profile. This problem is often overlooked, as the teeth are in contact throughout the involute profile. This causes the load to not be evenly distributed along the contact line. Consequently, it is important to consider the effect of misalignment on the contact force on the teeth of the spline coupling.
The centre of the male spline in Figure 2 is superposed on the female spline. The alignment meshing distances are also identical. Hence, the meshing force curves will change according to the dynamic vibration displacement. It is necessary to know the parameters of a spline coupling before implementing it. In this paper, the model for misalignment is presented for spline couplings and the related parameters.
Using a self-made spline coupling test rig, the effects of misalignment on a spline coupling are studied. In contrast to the typical spline coupling, misalignment in a spline coupling causes fretting wear at a specific position on the tooth surface. This is a leading cause of failure in these types of couplings.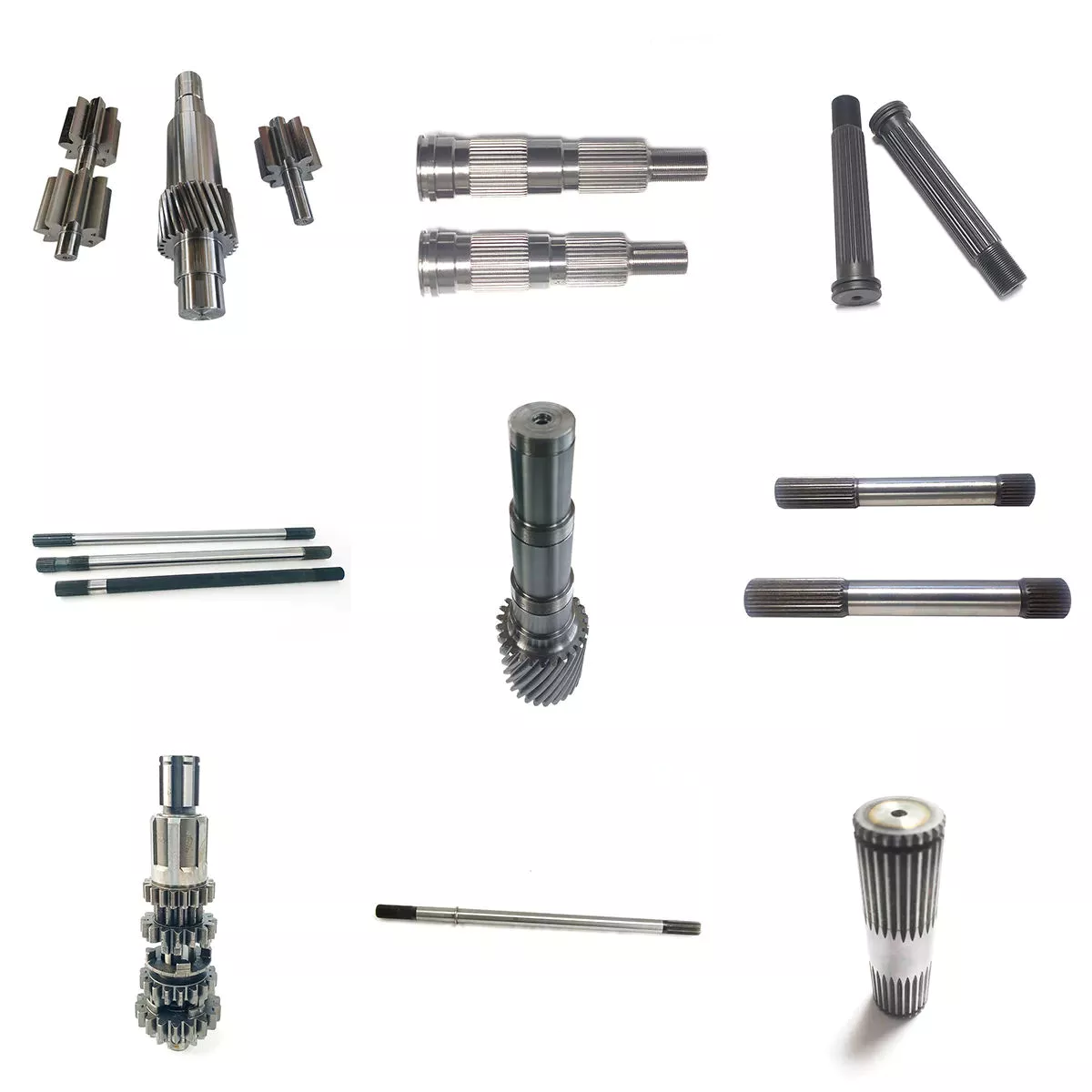
Wear and fatigue failure
The failure of a spline coupling due to wear and fatigue is determined by the first occurrence of tooth wear and shaft misalignment. Standard design methods do not account for wear damage and assess the fatigue life with big approximations. Experimental investigations have been conducted to assess wear and fatigue damage in spline couplings. The tests were conducted on a dedicated test rig and special device connected to a standard fatigue machine. The working parameters such as torque, misalignment angle, and axial distance have been varied in order to measure fatigue damage. Over dimensioning has also been assessed.
During fatigue and wear, mechanical sliding takes place between the external and internal splines and results in catastrophic failure. The lack of literature on the wear and fatigue of spline couplings in aero-engines may be due to the lack of data on the coupling’s application. Wear and fatigue failure in splines depends on a number of factors, including the material pair, geometry, and lubrication conditions.
The analysis of spline couplings shows that over-dimensioning is common and leads to different damages in the system. Some of the major damages are wear, fretting, corrosion, and teeth fatigue. Noise problems have also been observed in industrial settings. However, it is difficult to evaluate the contact behavior of spline couplings, and numerical simulations are often hampered by the use of specific codes and the boundary element method.
The failure of a spline gear coupling was caused by fatigue, and the fracture initiated at the bottom corner radius of the keyway. The keyway and splines had been overloaded beyond their yield strength, and significant yielding was observed in the spline gear teeth. A fracture ring of non-standard alloy steel exhibited a sharp corner radius, which was a significant stress raiser.
Several components were studied to determine their life span. These components include the spline shaft, the sealing bolt, and the graphite ring. Each of these components has its own set of design parameters. However, there are similarities in the distributions of these components. Wear and fatigue failure of spline couplings can be attributed to a combination of the three factors. A failure mode is often defined as a non-linear distribution of stresses and strains.


editor by czh 2023-02-21
China Professional Supplier of all kinds of Spare Parts for Hydraulic Motors and Hydraulic Pumps drive shaft components
Guarantee: 1 Year
Showroom Area: Germany
Excess weight: 6
Dimension(L*W*H): 20x10x15
Displacement: 110cm³
Pump Kind: PISTON PUMP
Optimum Stream Rate: 3100
Rotation: Right or remaining
Principle: push shaft
Shaft Kind: Spline Important
Normal or Nonstandard: Regular Hydraulic
Shipping and delivery TIME: Stock–within 2-3 Operating Days
Packaging Information: In wooden circumstance
Skilled Supplier of all kinds of Spare Components for Hydraulic Motors and Hydraulic Pumps
CZPT Sauer CZPT and CZPT all sorts of Construction spare parts
| Solution Name | Hydraulic Pump First parts |
| Model | A4VG56 A4VG71 A4VG90 A4VG125 90R75 90R100 90R100 K3V63 K3V112DT |
| Guarantee | 1 12 months |
| Availability: | in inventory |
| Application | Hydraulic Pump Hydraulic Motor |
Software
Hydraulic Pumps for machines with multi-circuit procedure these kinds of as excavators, cranes, ,Paver,drilling gear.
Firm Information
| Kawasaki | K3SP360,K5V80/a hundred and forty/a hundred and sixty/200,K3V63DT/140DT/180DT/280,K3VG280, |
| NV64/eighty four/111DT/137/172/270,NX15,NVK45, NMRV063 Worm Equipment Reducer Pace Ratio 7.5~a hundred RV030 Worm Gearbox Pace Reducer KVC925,KVC930,KVC932 | |
| M2X63/96/a hundred and twenty/146/one hundred fifty/one hundred seventy/210,M5X130/150/173/one hundred eighty/five hundred,MAG150/a hundred and seventy | |
| GM05VL/06VL/05VA/07VA,GM08/09/ten/17/eighteen/23/30H/35VA/35VL/38VB | |
| Rexroth | A2F A2FO A7V A6VM collection A4VSO45/71/one hundred twenty five/one hundred eighty/250/500, A4V40/56/seventy one, |
| A4VG28/40/forty five/50/56/71/ninety/125/a hundred and forty/one hundred eighty/250, A10VSO16/eighteen/28/forty five/63/71/eighty five/100/140, | |
| A10VSO28/45/63,A10V63,A11VG50, AKANTOR Bicycle Crankset MTB Highway Bike Crank Set Axis Sprocket Kit Bottom Bracket Chainwheel Bearing Chain Ring bicycle equipment A11V060/075/095/130/a hundred forty five/160/a hundred ninety/one hundred ninety/250,A11V260 | |
| Linder | HPV HPR B2PV BMV BPR collection |
| Uchida | A8VO sequence,AP2D12/sixteen/eighteen/21/25/36,A10VD40/43,A10V43,A10VE43 |
| Sauer | PV90R030/42/fifty five/75/100/180/250 |
| Eaton | 3321/3331,3322,4621/4631,5421/5431,3932-243,6423,7621 |
| Volvo | F11-28/39/571/one hundred fifty/250/060/080/090, 3D printer components shaft travel axle atv in robot line F11-a hundred and ten-MF-1H |
| Yuken | A16/37/forty five/56/70/ninety/a hundred forty five,MF16A |
| Vickers | PVE19/21/45/fifty seven/74/81/ninety eight/106/131/141, PVB 5/6/10/ten/fifteen/twenty/29, PVBQA29-SR, |
| PVQ40/50,PVB110 | |
| Parker | PVXS130/a hundred and eighty/250,PVXO250,PV250, |
| BMHQ30/PV180,PAVC038/65/a hundred,PZ075,PV090, Chain Sprocket Rotary Valve for Flour Procedure Industry Air Valve PV092 |
Packaging & Delivery
Rated Product:
| | ||
| Hydraulic Pump Spare parts | Hydraulic Motor | Hydraulic Pump Management valve |
How to Calculate Stiffness, Centering Force, Wear and Fatigue Failure of Spline Couplings
There are various types of spline couplings. These couplings have several important properties. These properties are: Stiffness, Involute splines, Misalignment, Wear and fatigue failure. To understand how these characteristics relate to spline couplings, read this article. It will give you the necessary knowledge to determine which type of coupling best suits your needs. Keeping in mind that spline couplings are usually spherical in shape, they are made of steel.
Involute splines
An effective side interference condition minimizes gear misalignment. When two splines are coupled with no spline misalignment, the maximum tensile root stress shifts to the left by five mm. A linear lead variation, which results from multiple connections along the length of the spline contact, increases the effective clearance or interference by a given percentage. This type of misalignment is undesirable for coupling high-speed equipment.
Involute splines are often used in gearboxes. These splines transmit high torque, and are better able to distribute load among multiple teeth throughout the coupling circumference. The involute profile and lead errors are related to the spacing between spline teeth and keyways. For coupling applications, industry practices use splines with 25 to fifty-percent of spline teeth engaged. This load distribution is more uniform than that of conventional single-key couplings.
To determine the optimal tooth engagement for an involved spline coupling, Xiangzhen Xue and colleagues used a computer model to simulate the stress applied to the splines. The results from this study showed that a “permissible” Ruiz parameter should be used in coupling. By predicting the amount of wear and tear on a crowned spline, the researchers could accurately predict how much damage the components will sustain during the coupling process.
There are several ways to determine the optimal pressure angle for an involute spline. Involute splines are commonly measured using a pressure angle of 30 degrees. Similar to gears, involute splines are typically tested through a measurement over pins. This involves inserting specific-sized wires between gear teeth and measuring the distance between them. This method can tell whether the gear has a proper tooth profile.
The spline system shown in Figure 1 illustrates a vibration model. This simulation allows the user to understand how involute splines are used in coupling. The vibration model shows four concentrated mass blocks that represent the prime mover, the internal spline, and the load. It is important to note that the meshing deformation function represents the forces acting on these three components.
Stiffness of coupling
The calculation of stiffness of a spline coupling involves the measurement of its tooth engagement. In the following, we analyze the stiffness of a spline coupling with various types of teeth using two different methods. Direct inversion and blockwise inversion both reduce CPU time for stiffness calculation. However, they require evaluation submatrices. Here, we discuss the differences between these two methods.
The analytical model for spline couplings is derived in the second section. In the third section, the calculation process is explained in detail. We then validate this model against the FE method. Finally, we discuss the influence of stiffness nonlinearity on the rotor dynamics. Finally, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method. We present a simple yet effective method for estimating the lateral stiffness of spline couplings.
The numerical calculation of the spline coupling is based on the semi-analytical spline load distribution model. This method involves refined contact grids and updating the compliance matrix at each iteration. Hence, it consumes significant computational time. Further, it is difficult to apply this method to the dynamic analysis of a rotor. This method has its own limitations and should be used only when the spline coupling is fully investigated.
The meshing force is the force generated by a misaligned spline coupling. It is related to the spline thickness and the transmitting torque of the rotor. The meshing force is also related to the dynamic vibration displacement. The result obtained from the meshing force analysis is given in Figures 7, 8, and 9.
The analysis presented in this paper aims to investigate the stiffness of spline couplings with a misaligned spline. Although the results of previous studies were accurate, some issues remained. For example, the misalignment of the spline may cause contact damages. The aim of this article is to investigate the problems associated with misaligned spline couplings and propose an analytical approach for estimating the contact pressure in a spline connection. We also compare our results to those obtained by pure numerical approaches.
Misalignment
To determine the centering force, the effective pressure angle must be known. Using the effective pressure angle, the centering force is calculated based on the maximum axial and radial loads and updated Dudley misalignment factors. The centering force is the maximum axial force that can be transmitted by friction. Several published misalignment factors are also included in the calculation. A new method is presented in this paper that considers the cam effect in the normal force.
In this new method, the stiffness along the spline joint can be integrated to obtain a global stiffness that is applicable to torsional vibration analysis. The stiffness of bearings can also be calculated at given levels of misalignment, allowing for accurate estimation of bearing dimensions. It is advisable to check the stiffness of bearings at all times to ensure that they are properly sized and aligned.
A misalignment in a spline coupling can result in wear or even failure. This is caused by an incorrectly aligned pitch profile. This problem is often overlooked, as the teeth are in contact throughout the involute profile. This causes the load to not be evenly distributed along the contact line. Consequently, it is important to consider the effect of misalignment on the contact force on the teeth of the spline coupling.
The centre of the male spline in Figure 2 is superposed on the female spline. The alignment meshing distances are also identical. Hence, the meshing force curves will change according to the dynamic vibration displacement. It is necessary to know the parameters of a spline coupling before implementing it. In this paper, the model for misalignment is presented for spline couplings and the related parameters.
Using a self-made spline coupling test rig, the effects of misalignment on a spline coupling are studied. In contrast to the typical spline coupling, misalignment in a spline coupling causes fretting wear at a specific position on the tooth surface. This is a leading cause of failure in these types of couplings.
Wear and fatigue failure
The failure of a spline coupling due to wear and fatigue is determined by the first occurrence of tooth wear and shaft misalignment. Standard design methods do not account for wear damage and assess the fatigue life with big approximations. Experimental investigations have been conducted to assess wear and fatigue damage in spline couplings. The tests were conducted on a dedicated test rig and special device connected to a standard fatigue machine. The working parameters such as torque, misalignment angle, and axial distance have been varied in order to measure fatigue damage. Over dimensioning has also been assessed.
During fatigue and wear, mechanical sliding takes place between the external and internal splines and results in catastrophic failure. The lack of literature on the wear and fatigue of spline couplings in aero-engines may be due to the lack of data on the coupling’s application. Wear and fatigue failure in splines depends on a number of factors, including the material pair, geometry, and lubrication conditions.
The analysis of spline couplings shows that over-dimensioning is common and leads to different damages in the system. Some of the major damages are wear, fretting, corrosion, and teeth fatigue. Noise problems have also been observed in industrial settings. However, it is difficult to evaluate the contact behavior of spline couplings, and numerical simulations are often hampered by the use of specific codes and the boundary element method.
The failure of a spline gear coupling was caused by fatigue, and the fracture initiated at the bottom corner radius of the keyway. The keyway and splines had been overloaded beyond their yield strength, and significant yielding was observed in the spline gear teeth. A fracture ring of non-standard alloy steel exhibited a sharp corner radius, which was a significant stress raiser.
Several components were studied to determine their life span. These components include the spline shaft, the sealing bolt, and the graphite ring. Each of these components has its own set of design parameters. However, there are similarities in the distributions of these components. Wear and fatigue failure of spline couplings can be attributed to a combination of the three factors. A failure mode is often defined as a non-linear distribution of stresses and strains.


editor by czh 2023-02-20
China massey ferguson tractor spare parts (PTO shaft) drive shaft center bearing
Situation: New
Warranty: 6 Months
Relevant Industries: Farms
Showroom Spot: None
Video outgoing-inspection: Not Accessible
Machinery Examination Report: Not Accessible
Marketing Kind: Normal Merchandise
Sort: Shafts
Use: Tractors
Tube: Triangle /Lemon /Star /Involute Spline Tube
Yoke: Splined yoke / Basic Bore yoke / Tube yoke
Yoke Processing: Forging or Casting
Plastic Guard: one hundred thirty/160/a hundred and eighty series
Color: yellow black and so forth.
Following Warranty Support: Movie technical assistance, On the web assist
Nearby Service Location: None
Packaging Information: 1 set for each carton or your need
Port: ZheJiang
Technical knowledge
Item
Packing
Firm Data
FAQ1. Q: Are your items cast or forged?
A: All of our merchandise are solid.
2. Q: Do you have a CE certification?
A: Of course, we are CE experienced.
three. Q: What’s the horse electricity of the pto shaft are obtainable?
A: We offer a entire variety of pto shaft, Hengyue ev rear finish electric truck axle rear wheel axle shaft ranging from 16HP-200HP.
4. Q: How several splined specification do you have ?
A: We make 1 3/8″ Z6 1 3/4″ Z6 1 3/4″ Z20 1 3/8″ Z21 hydraulic equipment pump KHP2B0 for agriculture equipment 1 1/2″ Z8 1 1/8″ Z6 48*42*8-Z8 sixty*fifty two*10-Z65*56*ten-Z8 SUGETOOLS Silver Dual Cylinder 12v Transportable Air Compressor Tire Inflator with Adapter for Automobile 54*46*9-Z8splines.
5. Q: What’s your payment terms?
A: T/T, L/C, D/A, XAS186C Aggressive value CZPT diesel portable air compressor utilised for water properly D/P….
six. Q: What is the shipping time?
A: 30 times soon after getting your superior deposit.
7. Q: What is your MOQ?
A: 50 sets for each type.
How to Calculate Stiffness, Centering Force, Wear and Fatigue Failure of Spline Couplings
There are various types of spline couplings. These couplings have several important properties. These properties are: Stiffness, Involute splines, Misalignment, Wear and fatigue failure. To understand how these characteristics relate to spline couplings, read this article. It will give you the necessary knowledge to determine which type of coupling best suits your needs. Keeping in mind that spline couplings are usually spherical in shape, they are made of steel.
Involute splines
An effective side interference condition minimizes gear misalignment. When two splines are coupled with no spline misalignment, the maximum tensile root stress shifts to the left by five mm. A linear lead variation, which results from multiple connections along the length of the spline contact, increases the effective clearance or interference by a given percentage. This type of misalignment is undesirable for coupling high-speed equipment.
Involute splines are often used in gearboxes. These splines transmit high torque, and are better able to distribute load among multiple teeth throughout the coupling circumference. The involute profile and lead errors are related to the spacing between spline teeth and keyways. For coupling applications, industry practices use splines with 25 to fifty-percent of spline teeth engaged. This load distribution is more uniform than that of conventional single-key couplings.
To determine the optimal tooth engagement for an involved spline coupling, Xiangzhen Xue and colleagues used a computer model to simulate the stress applied to the splines. The results from this study showed that a “permissible” Ruiz parameter should be used in coupling. By predicting the amount of wear and tear on a crowned spline, the researchers could accurately predict how much damage the components will sustain during the coupling process.
There are several ways to determine the optimal pressure angle for an involute spline. Involute splines are commonly measured using a pressure angle of 30 degrees. Similar to gears, involute splines are typically tested through a measurement over pins. This involves inserting specific-sized wires between gear teeth and measuring the distance between them. This method can tell whether the gear has a proper tooth profile.
The spline system shown in Figure 1 illustrates a vibration model. This simulation allows the user to understand how involute splines are used in coupling. The vibration model shows four concentrated mass blocks that represent the prime mover, the internal spline, and the load. It is important to note that the meshing deformation function represents the forces acting on these three components.
Stiffness of coupling
The calculation of stiffness of a spline coupling involves the measurement of its tooth engagement. In the following, we analyze the stiffness of a spline coupling with various types of teeth using two different methods. Direct inversion and blockwise inversion both reduce CPU time for stiffness calculation. However, they require evaluation submatrices. Here, we discuss the differences between these two methods.
The analytical model for spline couplings is derived in the second section. In the third section, the calculation process is explained in detail. We then validate this model against the FE method. Finally, we discuss the influence of stiffness nonlinearity on the rotor dynamics. Finally, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method. We present a simple yet effective method for estimating the lateral stiffness of spline couplings.
The numerical calculation of the spline coupling is based on the semi-analytical spline load distribution model. This method involves refined contact grids and updating the compliance matrix at each iteration. Hence, it consumes significant computational time. Further, it is difficult to apply this method to the dynamic analysis of a rotor. This method has its own limitations and should be used only when the spline coupling is fully investigated.
The meshing force is the force generated by a misaligned spline coupling. It is related to the spline thickness and the transmitting torque of the rotor. The meshing force is also related to the dynamic vibration displacement. The result obtained from the meshing force analysis is given in Figures 7, 8, and 9.
The analysis presented in this paper aims to investigate the stiffness of spline couplings with a misaligned spline. Although the results of previous studies were accurate, some issues remained. For example, the misalignment of the spline may cause contact damages. The aim of this article is to investigate the problems associated with misaligned spline couplings and propose an analytical approach for estimating the contact pressure in a spline connection. We also compare our results to those obtained by pure numerical approaches.
Misalignment
To determine the centering force, the effective pressure angle must be known. Using the effective pressure angle, the centering force is calculated based on the maximum axial and radial loads and updated Dudley misalignment factors. The centering force is the maximum axial force that can be transmitted by friction. Several published misalignment factors are also included in the calculation. A new method is presented in this paper that considers the cam effect in the normal force.
In this new method, the stiffness along the spline joint can be integrated to obtain a global stiffness that is applicable to torsional vibration analysis. The stiffness of bearings can also be calculated at given levels of misalignment, allowing for accurate estimation of bearing dimensions. It is advisable to check the stiffness of bearings at all times to ensure that they are properly sized and aligned.
A misalignment in a spline coupling can result in wear or even failure. This is caused by an incorrectly aligned pitch profile. This problem is often overlooked, as the teeth are in contact throughout the involute profile. This causes the load to not be evenly distributed along the contact line. Consequently, it is important to consider the effect of misalignment on the contact force on the teeth of the spline coupling.
The centre of the male spline in Figure 2 is superposed on the female spline. The alignment meshing distances are also identical. Hence, the meshing force curves will change according to the dynamic vibration displacement. It is necessary to know the parameters of a spline coupling before implementing it. In this paper, the model for misalignment is presented for spline couplings and the related parameters.
Using a self-made spline coupling test rig, the effects of misalignment on a spline coupling are studied. In contrast to the typical spline coupling, misalignment in a spline coupling causes fretting wear at a specific position on the tooth surface. This is a leading cause of failure in these types of couplings.
Wear and fatigue failure
The failure of a spline coupling due to wear and fatigue is determined by the first occurrence of tooth wear and shaft misalignment. Standard design methods do not account for wear damage and assess the fatigue life with big approximations. Experimental investigations have been conducted to assess wear and fatigue damage in spline couplings. The tests were conducted on a dedicated test rig and special device connected to a standard fatigue machine. The working parameters such as torque, misalignment angle, and axial distance have been varied in order to measure fatigue damage. Over dimensioning has also been assessed.
During fatigue and wear, mechanical sliding takes place between the external and internal splines and results in catastrophic failure. The lack of literature on the wear and fatigue of spline couplings in aero-engines may be due to the lack of data on the coupling’s application. Wear and fatigue failure in splines depends on a number of factors, including the material pair, geometry, and lubrication conditions.
The analysis of spline couplings shows that over-dimensioning is common and leads to different damages in the system. Some of the major damages are wear, fretting, corrosion, and teeth fatigue. Noise problems have also been observed in industrial settings. However, it is difficult to evaluate the contact behavior of spline couplings, and numerical simulations are often hampered by the use of specific codes and the boundary element method.
The failure of a spline gear coupling was caused by fatigue, and the fracture initiated at the bottom corner radius of the keyway. The keyway and splines had been overloaded beyond their yield strength, and significant yielding was observed in the spline gear teeth. A fracture ring of non-standard alloy steel exhibited a sharp corner radius, which was a significant stress raiser.
Several components were studied to determine their life span. These components include the spline shaft, the sealing bolt, and the graphite ring. Each of these components has its own set of design parameters. However, there are similarities in the distributions of these components. Wear and fatigue failure of spline couplings can be attributed to a combination of the three factors. A failure mode is often defined as a non-linear distribution of stresses and strains.


editor by czh 2023-02-19
China high quality Sinotruk spare parts gearbox Long Welded Shaft 12JSD200T-1707047 10JSD160-1707047-1RTD11609A-1707047 drive shaft assembly parts
Design: F4, Auman, Shacman, Howo, J5 Saloon, hanvan
Calendar year: 2 for Rapidly Transmission
Payment: TT/Paypal/Alipay
Packaging Particulars: Carton
Simply click for free quote Items Description
| Spot of Origin | China |
| Item Identify | Rapidly gearbox Welding shaft 12JSD200T-17571 |
| Software | FOR Quick GEARBOX FOR TRUCK |
| Top quality | Substantial-Good quality/Authentic |
| MOQ | 2pcs |
| Size | Common |
Analytical Approaches to Estimating Contact Pressures in Spline Couplings
A spline coupling is a type of mechanical connection between two rotating shafts. It consists of two parts – a coupler and a coupling. Both parts have teeth which engage and transfer loads. However, spline couplings are typically over-dimensioned, which makes them susceptible to fatigue and static behavior. Wear phenomena can also cause the coupling to fail. For this reason, proper spline coupling design is essential for achieving optimum performance.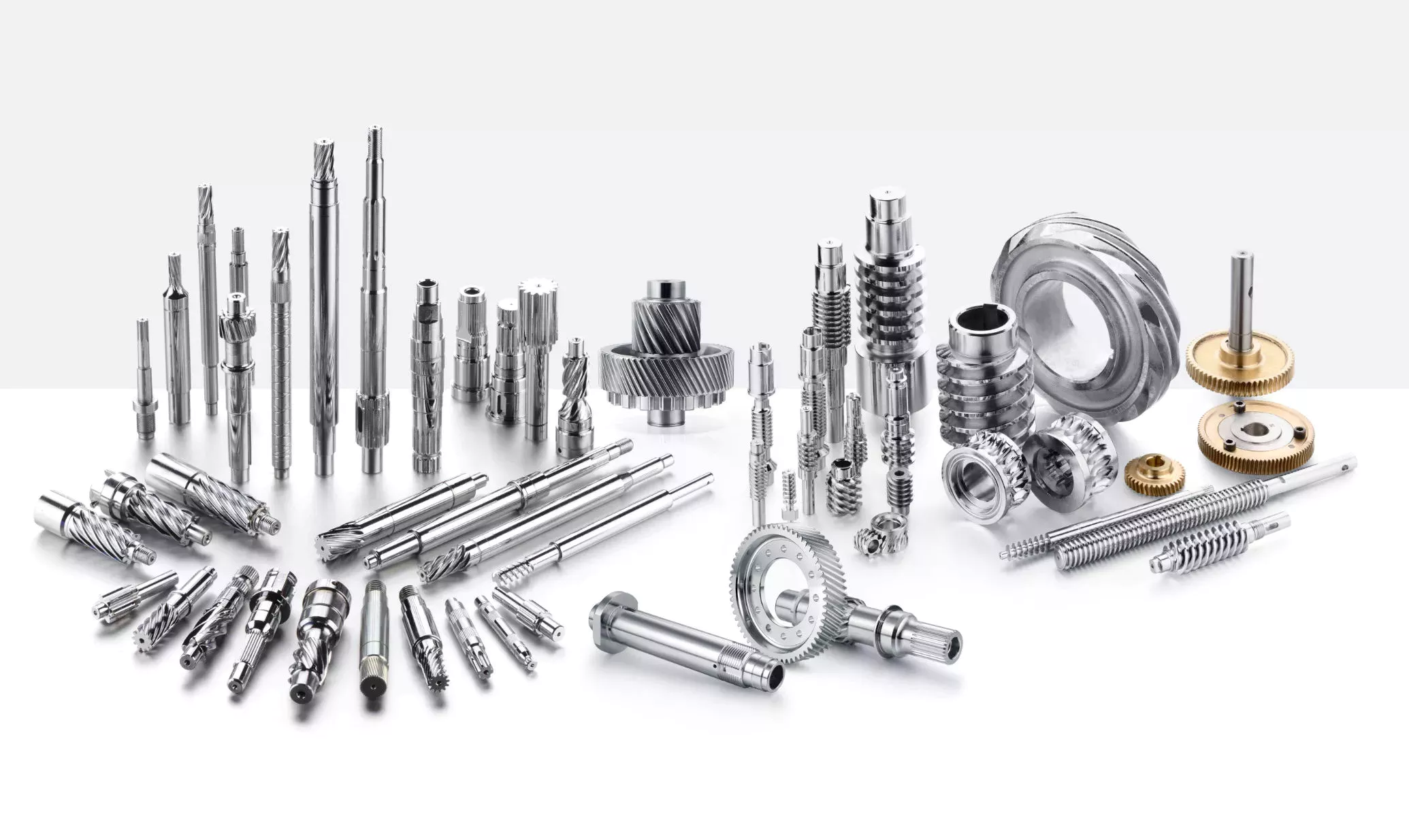
Modeling a spline coupling
Spline couplings are becoming increasingly popular in the aerospace industry, but they operate in a slightly misaligned state, causing both vibrations and damage to the contact surfaces. To solve this problem, this article offers analytical approaches for estimating the contact pressures in a spline coupling. Specifically, this article compares analytical approaches with pure numerical approaches to demonstrate the benefits of an analytical approach.
To model a spline coupling, first you create the knowledge base for the spline coupling. The knowledge base includes a large number of possible specification values, which are related to each other. If you modify one specification, it may lead to a warning for violating another. To make the design valid, you must create a spline coupling model that meets the specified specification values.
After you have modeled the geometry, you must enter the contact pressures of the two spline couplings. Then, you need to determine the position of the pitch circle of the spline. In Figure 2, the centre of the male coupling is superposed to that of the female spline. Then, you need to make sure that the alignment meshing distance of the two splines is the same.
Once you have the data you need to create a spline coupling model, you can begin by entering the specifications for the interface design. Once you have this data, you need to choose whether to optimize the internal spline or the external spline. You’ll also need to specify the tooth friction coefficient, which is used to determine the stresses in the spline coupling model 20. You should also enter the pilot clearance, which is the clearance between the tip 186 of a tooth 32 on one spline and the feature on the mating spline.
After you have entered the desired specifications for the external spline, you can enter the parameters for the internal spline. For example, you can enter the outer diameter limit 154 of the major snap 54 and the minor snap 56 of the internal spline. The values of these parameters are displayed in color-coded boxes on the Spline Inputs and Configuration GUI screen 80. Once the parameters are entered, you’ll be presented with a geometric representation of the spline coupling model 20.
Creating a spline coupling model 20
The spline coupling model 20 is created by a product model software program 10. The software validates the spline coupling model against a knowledge base of configuration-dependent specification constraints and relationships. This report is then input to the ANSYS stress analyzer program. It lists the spline coupling model 20’s geometric configurations and specification values for each feature. The spline coupling model 20 is automatically recreated every time the configuration or performance specifications of the spline coupling model 20 are modified.
The spline coupling model 20 can be configured using the product model software program 10. A user specifies the axial length of the spline stack, which may be zero, or a fixed length. The user also enters a radial mating face 148, if any, and selects a pilot clearance specification value of 14.5 degrees or 30 degrees.
A user can then use the mouse 110 to modify the spline coupling model 20. The spline coupling knowledge base contains a large number of possible specification values and the spline coupling design rule. If the user tries to change a spline coupling model, the model will show a warning about a violation of another specification. In some cases, the modification may invalidate the design.
In the spline coupling model 20, the user enters additional performance requirement specifications. The user chooses the locations where maximum torque is transferred for the internal and external splines 38 and 40. The maximum torque transfer location is determined by the attachment configuration of the hardware to the shafts. Once this is selected, the user can click “Next” to save the model. A preview of the spline coupling model 20 is displayed.
The model 20 is a representation of a spline coupling. The spline specifications are entered in the order and arrangement as specified on the spline coupling model 20 GUI screen. Once the spline coupling specifications are entered, the product model software program 10 will incorporate them into the spline coupling model 20. This is the last step in spline coupling model creation.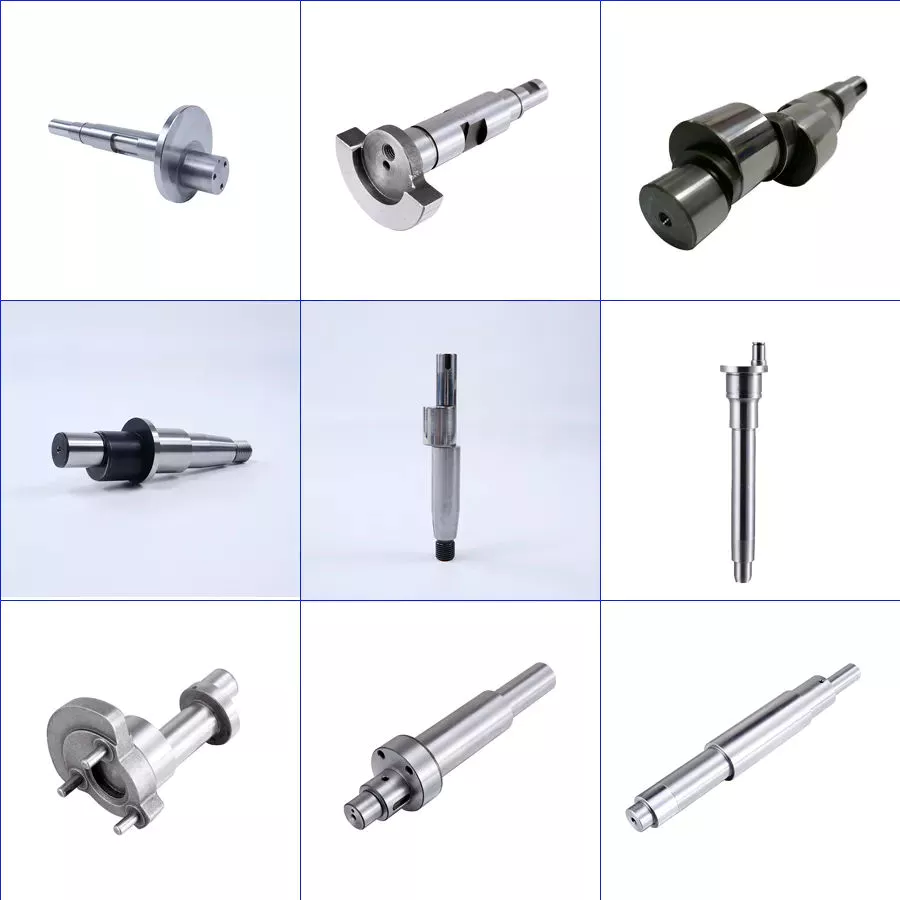
Analysing a spline coupling model 20
An analysis of a spline coupling model consists of inputting its configuration and performance specifications. These specifications may be generated from another computer program. The product model software program 10 then uses its internal knowledge base of configuration dependent specification relationships and constraints to create a valid three-dimensional parametric model 20. This model contains information describing the number and types of spline teeth 32, snaps 34, and shoulder 36.
When you are analysing a spline coupling, the software program 10 will include default values for various specifications. The spline coupling model 20 comprises an internal spline 38 and an external spline 40. Each of the splines includes its own set of parameters, such as its depth, width, length, and radii. The external spline 40 will also contain its own set of parameters, such as its orientation.
Upon selecting these parameters, the software program will perform various analyses on the spline coupling model 20. The software program 10 calculates the nominal and maximal tooth bearing stresses and fatigue life of a spline coupling. It will also determine the difference in torsional windup between an internal and an external spline. The output file from the analysis will be a report file containing model configuration and specification data. The output file may also be used by other computer programs for further analysis.
Once these parameters are set, the user enters the design criteria for the spline coupling model 20. In this step, the user specifies the locations of maximum torque transfer for both the external and internal spline 38. The maximum torque transfer location depends on the configuration of the hardware attached to the shafts. The user may enter up to four different performance requirement specifications for each spline.
The results of the analysis show that there are two phases of spline coupling. The first phase shows a large increase in stress and vibration. The second phase shows a decline in both stress and vibration levels. The third stage shows a constant meshing force between 300N and 320N. This behavior continues for a longer period of time, until the final stage engages with the surface.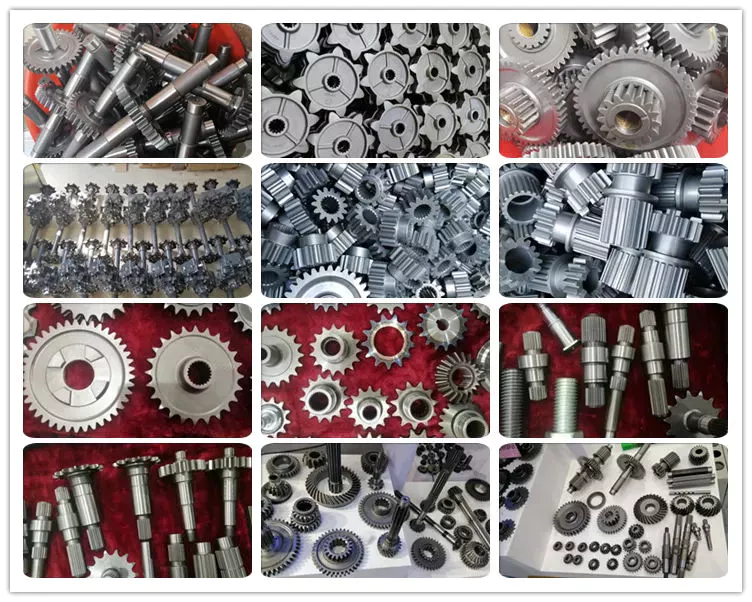
Misalignment of a spline coupling
A study aimed to investigate the position of the resultant contact force in a spline coupling engaging teeth under a steady torque and rotating misalignment. The study used numerical methods based on Finite Element Method (FEM) models. It produced numerical results for nominal conditions and parallel offset misalignment. The study considered two levels of misalignment – 0.02 mm and 0.08 mm – with different loading levels.
The results showed that the misalignment between the splines and rotors causes a change in the meshing force of the spline-rotor coupling system. Its dynamics is governed by the meshing force of splines. The meshing force of a misaligned spline coupling is related to the rotor-spline coupling system parameters, the transmitting torque, and the dynamic vibration displacement.
Despite the lack of precise measurements, the misalignment of splines is a common problem. This problem is compounded by the fact that splines usually feature backlash. This backlash is the result of the misaligned spline. The authors analyzed several splines, varying pitch diameters, and length/diameter ratios.
A spline coupling is a two-dimensional mechanical system, which has positive backlash. The spline coupling is comprised of a hub and shaft, and has tip-to-root clearances that are larger than the backlash. A form-clearance is sufficient to prevent tip-to-root fillet contact. The torque on the splines is transmitted via friction.
When a spline coupling is misaligned, a torque-biased thrust force is generated. In such a situation, the force can exceed the torque, causing the component to lose its alignment. The two-way transmission of torque and thrust is modeled analytically in the present study. The analytical approach provides solutions that can be integrated into the design process. So, the next time you are faced with a misaligned spline coupling problem, make sure to use an analytical approach!
In this study, the spline coupling is analyzed under nominal conditions without a parallel offset misalignment. The stiffness values obtained are the percentage difference between the nominal pitch diameter and load application diameter. Moreover, the maximum percentage difference in the measured pitch diameter is 1.60% under a torque of 5000 N*m. The other parameter, the pitch angle, is taken into consideration in the calculation.


editor by czh 2023-02-18